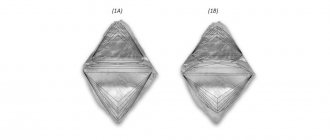
Precious variety of corundum
Natural corundum is a very hard mineral, second only to diamond in hardness. Corundum is a mineral which is also called ruby and sapphire which are very expensive stones and that is why corundum stone is used in jewelry. Ruby corundum is a red-colored variety of corundum mineral, and any corundum mineral of a different color is classified as sapphire.
Red corundum stone
The word corundum comes from the ancient Hindu word korund, which is unknown what it meant, but it was later used to refer to stones brought from India to Europe. In its pure form, this mineral is colorless, but due to the presence of other minerals in its composition, corundum acquires color. In its pure colorless form, the mineral is very rare in nature, but other varieties of corundum such as yellow, green, blue, lilac, white, violet are very common.
Yellow corundum is a natural stone
Yellow corundum has the greatest hardness. However, if you look closely at the color of corundum, it becomes clear that it consists of layers of different colors that give the stone a certain shade. For example, purple corundum consists of a large number of blue and red layers, and blue corundum consists of yellow and blue layers. Some stones have a special crystal structure, and if they are cut into a cabochon, this structure will produce a bright, light six-pointed star. In nature, precious corundum is mainly found in small sizes. Very often, very fine, usually in powder form, is used in industry as an abrasive material.
Blue corundum stone photo
Corundum has the chemical formula Al2O3, and in its chemical composition it is alumina with an admixture, that is, aluminum oxide and a small amount of chromium, ferric iron and other metals. The red color of the stone is mainly given by chromium, and the blue color is given to the stone by titanium. Of the red flowers, the most valuable color is considered to be pigeon's blood, a red color that has a faint purple tint. The spectrum of red colors is very large and therefore, in order to create a color boundary between rubies and sapphires, starting with light red color, stones are classified as sapphires.
Purple corundum stone photo properties
The colorless transparent variety of corundum does not give a reflection and therefore such stones are not of interest to jewelers. Corundum crystals belong to the holohedral class of trigonal system. Corundum crystal lattice is usually found in two types. The first type includes rubies in which the crystal has large faces and is found in the shape of a triangle related to the basopinacoid in combination with six faces of a prism and six faces of the main rhombohedron. The second type includes sapphires in which the crystal has twelve pyramid faces that form an equatorial belt.
Corundum green
- Almost all precious varieties of corundum have a birefringence of 0.008, and green corundum can have even 0.009.
- The refractive index for an ordinary ray ranges from 1.768 to 1.778, and for an extraordinary ray from 1.76 to 1.77. Since the refractive index of an extraordinary beam is less than that of an ordinary one, any type of corundum is optically negative.
- It has one optical axis which is located perpendicular to the basopinacoid and parallel to the edges of the prismatic faces.
- The variance for the interval B - G is 0.018.
- It has a distinct and characteristic dichroism, which for an ordinary beam appears in a deep and beautiful color, and for an extraordinary beam it appears in a pale color. Corundum of blue color for an ordinary ray has a deep blue color, and for an extraordinary ray it has a yellowish-blue color. Red corundum for the ordinary ray has a deep purple-red color, and for the extraordinary ray it has a pale yellowish-red color.
- When heated, corundum becomes lighter in appearance, causing pale purple and yellow stones to become colorless and purple stones to become pink.
- When irradiated, its color becomes saturated and even colorless ones can acquire some color depending on the chemical composition of corundum.
- Transparent corundum has a glassy luster.
- Red stones have a fluorescent doublet that is located in the red region of the visible spectrum.
- The density of corundum ranges from 3.94 to 4.1.
- The hardness of corundum on the Mohs scale is number 9.
- It has a separation that is usually parallel to the plane of the basopinacoid and in rare cases parallel to the faces of the main rhombohedron.
When processing corundum, close attention must be paid to the symmetry of the crystal. Previously, they were given a step cut, but nowadays they are given a diamond and mixed cut, that is, diamond on top and step on the bottom. The use of corundum is developed not only in jewelry but also in watches, high-precision instruments and even as an abrasive material. Large red corundum stones are very rare in nature and therefore are very expensive, while large precious blue corundum stones and stones of other colors are more common and therefore they are cheaper than red ones.
Pink corundum
The British Museum displays several examples of historical large corundum wares;
- The sapphire rose from the collection of Sir Gus Sloan has an octagonal outline. It is 19 mm in diameter and weighs 31.5 carats. This rose, along with other rubies and emeralds, adorned a quartz button.
- A corundum crystal in the shape of a Buddha figurine is attached to a gold pin.
- Broken Burmese ruby crystal. This stone weighs 690 grams and measures 12 cm across. This stone is brilliant cut above the waist and step cut below. It formerly belonged to the Duke of Devonshire.
Russian regalia include stones such as;
- Cornflower blue sapphire weighing 250 carats. This stone is 2.2 cm high and varies in diameter from 3 to 3.4 cm.
- Corundum is a red stone in the shape of a pigeon egg. This stone belonged to King Gustav Adolf of Sweden. In 1777, during the visit of the King of Sweden to St. Petersburg, he presented this stone to Empress Catherine II. It later turned out that this was a pink tourmaline of medium quality weighing 250 carats. Currently it is in the diamond fund in Moscow.
In Paris, the Jardin des Plantes collection contains two untreated sapphires.
- The first brownish color was called Rospoli. It weighs 135 carats.
- The second measures 5 cm in length and 3.8 cm in thickness.
There are several stones in the American Museum of Natural History in New York.
- A large sapphire weighing 163 carats and a yellow one weighing 100 carats were found in Ceylon.
- A purple stone brought from Thailand weighing about 34 carats.
- Also in this museum there is a golden-yellow stone that weighs 75.4 carats.
- The museum also houses 3 largest star stones. The first star corundum is the Edith Haggin de Long ruby, weighing 100 carats. Its dimensions are 3.8 cm in length and 2.5 cm in diameter. The second star sapphire, the Star of India, weighs 563 carats. The third star sapphire is the lilac Midnight Star, weighing 116 carats.
Ruby can easily be confused with spinel or almandine garnet. But spinel, like almandir garnet, does not have birefringence and therefore can be easily distinguished from corundum. Also, natural corundum stone can be easily distinguished from other stones by its high density and bright lines in the absorption spectrum.
Sapphire corundum is a natural stone
In nature, corundum deposits occur in the form of veins and segregations of various igneous rocks, as well as as a product of contact-metamorphic processes. The most valuable stones are found as crystals in crystalline limestones or as pebbles in alluvial deposits. Almost all rubies are found in ruby mines that are located near Mogok located in upper Burma, approximately 145 km northeast of Mandalay at an altitude of approximately 1200 meters above sea level. In 1929, a large corundum weighing 958 carats was found on the surface of the earth directly under the grass cover. This stone was called the Jewel of the Jungle. The jewelers did not know how to cut this sapphire and as a result they divided it into 9 parts. Good red stones are found in Thailand near Bangkok. Thai stones are much darker than Burmese stones and therefore experts can determine their deposit by their color. Brown corundum with a characteristic silky structure is also found in Thailand. In India, stones in the form of sapphires are found in different places, but the largest deposit of corundum is considered to be the Zaskar Range, which is located in the northwestern Himalayas in Kashmir. In the USA, in the state of Montana, deposits of corundum were discovered in the form of sapphires that retain their color under artificial light, and in the state of North Carolina, about 10 km north of Franklinton, red corundum of medium quality was found near the Cowie Creek. In Australia, near Anaka in Queensland, jewelry corundum of all types was discovered. In Zambia, near Samobula, stones are also occasionally found in productive pebbles. In Tanzania, 80 km from Tanza on the Umba River, opaque ruby corundum was found.
How is the weight of precious minerals measured?
The main measure of gemstone weight is carat. It is equal to 1/5 of a gram. This unit is sometimes called the metric carat. It is worth distinguishing the unit of measure for precious gems from the measure of quality and purity of gold jewelry alloy. In Russian the abbreviation kar is accepted, in English - ct.
For natural pearls, a separate unit for measuring weight is used - gran. It is equal to a quarter of a carat. In Japan, a unit of mass is sometimes used, the momme. For the smallest diamond samples, a unit called a point is used. Raw jewelry raw materials are measured in grams. When weighing semi-precious and ornamental stones, grams are also used. In Europe, weight is sometimes indicated in ounces. When measuring the mass of a gem, two digits after the decimal point are taken into account, the value of the third is ignored. The cost of a mineral is calculated by multiplying the unit price by the weight of the sample. As the weight increases, the carat price also increases, since large diamonds are very rare. But this rule applies only to precious minerals. The price of a certain gem depends only one third on its weight. The main components are the quality of the mineral, its color, transparency and the skill of the cutter.
The most famous of the large diamonds is called the Star of Africa. Its weight in carats is 530.20, and in grams - 106, it is made in the shape of a drop and has 74 facets.
Historically, people used grains of the most common cereals or seeds to determine the mass of very small objects. In Europe it was barley grain, and in the countries of the East it was acacia seed. According to some sources, the word “carat” got its name from the Greek “keration” - “small horn”. This is what acacia seeds were called in the Mediterranean, which served local jewelers as weights for weighing gold and jewelry. The average weight of one seed is 200 mg.
For a long time, carats had different weights in different countries. Because of this, there are discrepancies in the description of the characteristics of many antique diamonds . For example, a stone cut and weighed in London turned out to be several units less than the specified weight in Florence. The carat could weigh from 188 to 217 mg. In 1907, a metric carat equal to 200 mg was approved in Paris. But it was only in 1914 that it was recognized by the bulk of jewelers and sellers of precious stones around the world.
To determine the mass of a stone mounted in a product, you do not need to remove it from the frame. Special templates have been developed with which you can weigh a brilliant-cut diamond or pearl. The most accurate way is to measure with calipers. The weight is calculated using Charles Meaux's tables, which take into account the stone's deviations from the ideal cut shape. Jewelers call the smallest diamonds (0.07 - 0.15 ct) "melange" or "mele", stones from 0.3 to 1 are medium, from 1 ct - large.