What's included
Since not all women and girls can afford to wear items made of gold, silver or platinum, jewelers use costume jewelry to make more affordable jewelry. What it is? The photos presented in the article demonstrate the varied beauty made from this material. These can be beads, earrings, clips, rings, bracelets, hair decorations (hairpins, headbands, crabs), brooches, etc.
When making an alloy, tin is most often used as a base. In its natural form, it is not suitable for the production of forged products, since it is refractory and brittle. Therefore, since ancient times, other metals have been added to tin. What else can be included in the alloy? This includes aluminum, copper, antimony, and any other metal that has hypoallergenic qualities and does not irritate human skin. When copper is added, the alloy becomes ductile, and antimony maintains the bright and sparkling appearance of the product for a long time.
Sometimes manufacturers use zinc as a basis in order to reduce the cost of jewelry. However, the appearance will be strikingly different from pewter.
Characteristics of popular jewelry alloys
Gold, platinum, silver, palladium and other precious metals are very rarely used in their pure form in the jewelry industry. And this is not always due to the high cost of noble materials and the need to make jewelry more affordable. Much more often, by adding various impurities, the strength, reliability and other performance characteristics of the finished product increase. For example, gold is a very soft metal and, in its pure form, easily deforms even with minor impact. Of course, such decoration will not last long. And silver without additives oxidizes and darkens faster.
Another reason why noble metals are enriched with various additives is to increase their decorative properties. If we consider the same gold, then thanks to additives, manufacturers can give it a white, green, pink tint.
Samples of precious metals
To designate the weight units (quantities) of the main noble material in relation to the alloying components in the alloy, the concept of sample is used. The digital value is determined per 1 kilogram of microscopically homogeneous jewelry metal mixture.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, each piece of jewelry or other product made of precious metals must have a hallmark. The alloy content is controlled at the state level by the relevant Government decree.
- Gold (Au) alloys. Samples 958, 750, 585, 500 and 375. Products may contain copper, silver, zinc and other impurities. Hardness and melting point depend on the alloy. “Colored” gold is often called a metalloid. In addition, some shades have their own designation. For example, an alloy with aluminum in a ratio of 78.5% to 21.5%, which produces a metal with an expressive purple-violet color, is known as “Amethyst Gold”. 750 gold alloy weighs approximately 15-20% heavier than 585 alloy, which, combined with the higher gold content, significantly increases the price of the product.
- Silver alloys. In the jewelry industry, 999, 960, 925, 916, 875, 830 and 800 are found. The metal may contain copper (gives a yellowish or reddish tint) and other impurities. All materials have a high degree of malleability and ductility.
- Platinum (Pt) alloys. Samples 950, 900 and 850. Platinum is a noble metal and is highly resistant to corrosion. High purity platinum alloys weigh 75-80% more than 585 gold alloy, which leads to a very high cost of the product (about 3 times higher), despite the fact that a gram of platinum costs less than a gram of gold. In addition, platinum is the softest of jewelry metals, which negatively affects the durability of platinum products.
- Palladium (Pd) alloys. Russian jewelry can be 850 or 500 standard. Metal alloys are characterized by an intense white tint and high resistance to tarnishing in air. Palladium, like platinum, is a noble metal of the platinum group. The advantages of palladium over white gold are its natural white color and hypoallergenicity (nickel contained in white gold alloys can cause irritation). The advantages of palladium over platinum are its lower price and weight, comparable to the weight of 585 gold alloy, as well as higher hardness and durability of products.
- Other platinum metals. In addition to platinum and palladium, the group of noble platinum metals also includes iridium (Ir), rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru) and osmium (Os). These metals have very high hardness and price, which allows them to be used as alloy additives in platinum and palladium alloys. Rhodium is also used as an electroplate for white gold to give it a whiter color, luster and durability.
Modern alloy sampling systems
Metric system of samples. Operates in Russia from 1927 to the present. It was adopted during the transition to world mass units instead of the spool system. When calculating, it is established that 1 kilogram of pure precious metal corresponds to 1000 samples. The metric method is considered one of the most convenient and visual.
For example, 1 kilogram of 925 silver alloy consists of 925 grams (92.5%) of the noble metal and 75 grams (7.5%) of the alloy.
Carat sample system. The method has German roots and is used only for alloys that contain gold. The content of pure precious metal is determined by the number of carats in one “Cologne mark” (a conventional unit of historical origin). In this case, the maximum standard will correspond to 24 ct; you can also find values of 22, 18, 14, 12 and 9. It should be remembered that 1 carat is equal to 9.7 g, and the Cologne mark is 233.8 g.
For example, if the fineness of a piece of jewelry is 14 ct, then it contains 14 karats of gold and 10 karats of ligature.
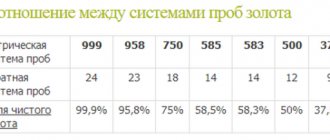
Correspondence of carat and metric hallmarks for gold products
| Carat samples | 24 | 23 | 18 | 14 | 12 | 9 |
| Metric samples | 1000 | 958 | 750 | 585/583 | 500 | 375 |
Comparative characteristics of alloy hardness
To measure the hardness of jewelry alloys, the Vickers method is used, which is regulated by GOST 2999-75 and the international standard ISO 6507. The method involves pressing a tetrahedral diamond pyramid into the test material, the angle between the opposite faces of which is 136°.
To calculate hardness, a formula is used that allows you to find the desired value by dividing the load P by the area of the resulting pyramid imprint. The value is designated by the letters HV and is dimensionless.
Comparative table of hardness of jewelry alloys
| Name | Compound | Hardness | Main characteristics |
| Pd950/Ru (American palladium alloy) | 95% palladium + 5% ruthenium | 130 HV | has nobleness and high hardness, the price of ruthenium is extremely high |
| Pt950/Cu | 95% platinum + 5% copper | 110 HV | golden mean in price and quality |
| Pt950/Ir | 95% platinum + 5% iridium | 80 HV | the surface is very easily damaged, very expensive |
| Pt900/Ir | 90% platinum +10% iridium | 100 HV | scratches easily, very expensive |
| Pt950/Co | 95% platinum + 5% cobalt | 135 HV | not noble (magnetic, oxidized), dear |
| Pd850/AgCu | 85% palladium + silver + copper | 100-120 HV | not noble, cheap |
| Pt1000 | pure platinum | 40 HV | extremely soft material, scratches remain on the surface |
| 750 gold alloy multi-component | 75% gold + 25% impurities (silver, copper, palladium, zinc, nickel) | 155 HV | hard enough, non-oxidizing, expensive |
| Multi-component 585 gold alloy | 58.5% gold + 41.5% impurities (silver, copper, palladium, zinc, nickel) | 125 HV – 165 HV | depending on the type of ligature, it may have different hardness and price |
| Multi-component 375 gold alloy | 37.5% gold + 62.5% impurities | 120 HV | quite hard, polishes well, cheap |
| Silver 925 | 75 HV | Soft metal, oxidizes, easily damaged |
Forbidden additives
It is noteworthy that already in the 19th century, jewelry alloy was widely used, the composition of which also included lead until the end of the century. But when scientists discovered that it remained on the skin, this additive was strictly banned. Today, the absence of lead in such alloys is prescribed at the legislative level.
Another forbidden metal that should never be in a good jewelry alloy is nickel. The reason for this is the negative effect of metal on the skin, which can result in an allergic reaction.
Gold samples
The amount of pure gold content in the alloy can be determined by the sample stamped on the product. In Russia, a metric standard is used: its value indicates the number of grams of pure noble metal in one kilogram of alloy.
- 958 standard
contains up to 96.3% pure gold. This alloy includes silver and copper as alloying components. It is very resistant to external influences, retains polish well, but is very flexible. 958 gold has a rich, bright yellow hue. It is mainly used to make wedding rings and pendants. - 750 standard
is the second most popular gold alloy. It contains up to 75.5% of noble metal, and other components are silver, platinum, palladium, nickel, copper. This alloy is durable and highly polished, so 750 gold items are durable and have a beautiful shine. - 585
is the most popular alloy in jewelry production. It contains up to 59% pure gold and includes shares of silver, palladium, nickel, copper, and zinc. 585 gold is quite hard and durable, it practically does not tarnish. The range of shades is wide - from white, red and yellow to various shades of green, depending on the proportion of metals added. - 500 and 375 samples
are practically not used in jewelry production. 375 standard is usually called a gold-containing alloy of silver and copper. Such gold tarnishes quite quickly in air, which significantly limits its use.
Despite the large palette of possible shades of gold, the most popular are still yellow, red and white gold.
Yellow gold
Its intense color most closely resembles that of native gold, which has long been used to create truly royal jewelry. But pure gold is not very practical jewelry: due to its softness, products made from it are not suitable for everyday wear.
The addition of a ligature significantly increases the wear resistance of gold products. 585 yellow gold allows jewelers to make jewelry of varying degrees of complexity. At the same time, they remain wear-resistant and do not lose their attractiveness.
Red gold
Red gold is obtained by adding an alloy containing some copper and zinc to the precious metal. The more copper is added to the alloy, the more intense the red hue the finished product acquires. If up to 10% palladium is added to the alloy, this gives the gold an even deeper red hue. Conversely, a small amount of silver in the alloy softens the red color, making it more noble. Jewelers value red gold for its exceptional strength, which allows them to create airy, openwork jewelry without fear of deformation. Red gold rings and pendants, created at the end of the 19th century, still retain their beauty and elegance.
What does the appearance say?
Jewelry craftsmen can simply figure out by eye what the jewelry alloy is made of. If the color of the product is slightly dull and matte, then tin plays the “main violin” in the composition. This decoration will be light, but brittle. If there is a reddish tint, then the alloy contains copper. In this case, the color will change slightly, since the aged look was originally intended. A yellow-green (sometimes yellow-gray) shimmer indicates the presence of brass in the composition.
Some jewelry alloys contain steel, and jewelry made from it has a corresponding gray, metallic tint or made to look like silver based on chromium. If the alloy product is too dark in color, this indicates the addition of nickel, which causes allergies in sensitive people. Less common are titanium alloys, which give jewelry durability and strength, but are many times more expensive.
Types of jewelry alloys
Precious and base metals that make up the jewelry alloy are indicated in the markings. The most popular ones have their own designation, the rest are marked with the abbreviation “Ost.” An example of the letter designations of components according to the current GOST: Zl (gold), Sr (silver), Rd (rhodium), Pl (platinum), Pd (palladium), C (zinc), M (copper), N (nickel).
From gold
The cost, color and shade of the product depend on the alloy components and the ratio of alloying components. Thanks to its ductility and beauty, gold never goes out of fashion. Jewelry is constantly evolving, and the use of new additives makes it possible to create gold jewelry of unusual colors.
For the needs of jewelers, metallurgical enterprises produce gold bars, semi-finished products, and rolled products. The finished products are marked with an alphanumeric designation. It is easy to understand from the labeling how many main and additional components are in the composition.
- The composition of the two-component alloy ZlM-585 includes Au (58.5%) and Cu (41.5%). Thanks to copper, the products have a reddish tint and good wear resistance. It increases hardness and lowers the melting point of raw materials.
- The three-component , popular in Soviet times, is still in trend - ZlSrM 585−80 (58.5% - Au, 8% - Ag, 33.5% - Cu).
- ZlSrM-200 has a straw or bright lemon color. It contains Au, as in any 585 precious metal, 58.5%, and the ratio of copper and silver is 21.5% Cu, 20% Ag.
- Unusual green jewelry is made from ZlSr 585-415 (58.5% Au, 41.5% Ag). Jewelers rarely use this type of raw material; products made from it are difficult to repair, it has low hardness and a high melting point.
- Formula of expensive 585 white gold: 58.5% - Au, 25.5% - Ag, 16% - Pd (ZlSrPd 585-255-160). Palladium gives the metal an attractive white color.
- The formula of less expensive white gold is: 58.5% Au, 21.5% Cu, 12.5% Ni, 4% Zn. Zinc brightens, and nickel improves the casting properties of jewelry raw materials.
For people sensitive to impurities, it is better to purchase jewelry made of high-grade gold (958 standard)
Gold products of unusual colors (purple, blue, black) are created from raw materials made using special technologies using intermetallic compounds.
Made of silver
The precious metal itself oxidizes and darkens. To improve the properties, manufacturers include non-ferrous metals in the master alloy: zinc, copper, nickel, cadmium. The following brands of silver alloys are used as raw materials for the production of men's and women's jewelry:
- СрМ 800 (80% - Ag, 20% - Cu);
- СрМ 830 (83% - Ag, 17% - Cu);
- СрМ 875 (87.5 - Ag, 12.5% - Cu);
- СрМ 925 (92.5 - Ag, 7.5% - Cu);
- СрМ 960 (96% - Ag, 4% - Cu).
A large percentage of copper gives the precious metal a yellowish tint. Raw materials with a high silver content are used for fine filigree work, blackening, and enameling .
From platinum
The composition of the alloy includes palladium, cobalt, copper, rhodium, and iridium. Alloying elements improve casting properties and adjust the physical characteristics of the metal:
- cobalt improves mechanical properties;
- iridium and rhodium increase hardness;
- copper affects strength and hardness;
- palladium affects ductility.
of 900 and 950 standard are used in jewelry .
Rings, earrings and rings made of platinum have a low wear rate. Neutral grayish-white shades highlight the exquisite beauty of precious and semi-precious stones.
Coating options
Often, finished products are coated with various compounds, since the jewelry alloy contains metals that lead to darkening. For example, for a bright, expensive shade, gilding or silver plating is chosen, and for an interesting antique color, it is coated with copper or bronze. Brass and chrome plating is more often seen not on jewelry, but on furniture accessories. And such an option as gold leaf is used by craftsmen as a covering for church domes, decorative frames for icons, pectoral crosses, etc.
Advantages
All products for the manufacture of which jewelry alloy is used have a number of positive characteristics. If we talk about jewelry, then everyone knows the fact that costume jewelry is much cheaper in price than products made from precious metals and stones. It is characterized by wide availability, as it is sold in many stores and supermarkets. Health safety is no less important: the alloy composition does not contain any elements that irritate the skin, so the products can be worn by almost everyone.
Precious metals and their alloys
Precious metals. Gold
All metals that occur in our nature have certain physical and chemical characteristics. These characteristics determine the properties of metals (thermal conductivity, density, hardness, chemical reactivity, and others). According to general parameters of properties, metals are divided into groups (ferrous, non-ferrous, noble precious and others) and are used in various fields of industry.
The group of noble precious metals includes 8 metals - gold, silver, platinum and platinum group metals (platinoids) - palladium, rhodium, iridium, ruthenium and osmium. They are quite stable in the air (do not oxidize), have high resistance to aggressive environments (acids, alkalis, etc.), softness, plasticity, go well with colored precious stones and enamels, and are easily combined with each other and with other materials. Due to these properties, metals of this group are widely used in jewelry. At the same time, the main materials for making jewelry are actually four metals - gold, silver, platinum and palladium. Other metals (for example, rhodium) are used as protective and decorative coatings or additives in alloys. This is explained by the fact that the use of pure metals in jewelry production is irrational due to their insufficient wear resistance, hardness, and high cost.
In the manufacture of jewelry for various purposes, other metals are added to precious metals in certain proportions, which are called alloying metals, or alloy (alloying metals can be both precious and base metals). In this way, metals are given the properties necessary for further use in production. This may be a change in color, a decrease or increase in ductility, an increase or decrease in hardness, or a change in the melting point. The resulting mixtures are called precious metal alloys.
Precious metals. Palladium
Alloys of precious metals are usually distinguished by composition and technological characteristics. Alloys are named depending on the main component (gold alloys, silver alloys, etc.). According to technological characteristics, or application, alloys are intended for handwork, stamping, casting or soldering.
The amount of precious metal in an alloy is called fineness.
Fineness is a digital value indicating the content of pure precious metal in grams in 1 kilogram (1000 g) of a jewelry alloy (example: gold (750°) - 1 kilogram of a 750 fine jewelry alloy contains 750 grams of pure gold, the rest are alloying components, eg silver, copper, etc.).
A hallmark is assigned to each jewelry alloy . The content of pure metal in alloys intended for commercial production is established by the state. In Russia, the following standards are established for jewelry made of precious metals: for gold - 999, 958, 750, 585, 500 and 375; for silver - 999, 960, 925, 875, 830, 800; for platinum - 950, 900 and 850; for palladium - 850 and 500. The number of jewelry alloys is constantly growing as new technologies in jewelry production develop. The alloys that are most widespread in Russia are provided for by GOST R 30649-99.
Comments on the publication “Precious metals and their alloys”
Flaws
In addition to positive qualities, jewelry alloy also has negative ones. So, it cannot withstand constant bending and may break. Also, any product made from such an alloy does not have long-term wear resistance and, if exposed to an aggressive environment, quickly changes its appearance and becomes unusable. For example, women often swim in the sea without taking off their rings and earrings. But salty sea water immediately begins the process of destruction. If they are made of a jewelry alloy, then at best they can simply change color. Any acid and alcoholic drinks have an even worse effect. You can put food vinegar, any detergents and even some medications on a par with the previous destroyers. In no case should manganese come into contact with the alloy, because it is very difficult to wash off.
Rules of care
When buying jewelry in stores, fashionistas often ask: does jewelry alloy darken or not? The answer is simple: it darkens under the influence of the external environment. Even with daily contact with the skin, a reaction may occur and the alloy will tarnish. The only exception here is products with a durable galvanic coating.
How should you care for accessories made of jewelry alloy? You should not allow contact with water, soap and shampoos, various chemicals, you should avoid temperature changes, and protect from hairspray, perfumes, and deodorants due to the content of acidic substances in them.
How to clean up falling debris and dirt? Cotton, flannel or special fabric napkins are used. To prevent deformation, you need to remove jewelry when playing sports (running, swimming, fitness), as well as when performing repairs, especially when working with paints and varnishes.
Products must be stored separately from each other to avoid a chemical reaction between them.