| Category | Beryls |
| Title in English | Emerald |
| Formula | Be3Al2Si6O18 |
| Group | Beryl group |
| Color | Yellowish-green, Green |
| Stroke color | White |
| Shine | Glass |
| Transparency | Transparent, Translucent |
| singonia | Hexagonal |
| Hardness | 7,5 — 8 |
| Cleavage | Imperfect |
| Density, g/cm³ | 2,69 — 2,78 |
| Kink | Conchoidal, Uneven |
| origin of name | Emerald jewelry was sold back in Babylon, and this is the 3rd millennium BC. Although, historians say that evidence has been found that emerald mining was carried out back in the 19th century BC. The field was located near the Red Sea and was controlled by the Egyptians. Due to the fact that humanity has long been familiar with this precious stone, the history of the emergence of the term “emerald” is rooted in the deep past. The modern form of the Russian word emerald owes its appearance to the Turkish word zümrüt. It, in turn, comes from the Persian zumurrud. But the Persians have already borrowed their version from Greek. The Greeks used the term σμάραγδος or smaragdos - green stone. It is interesting that even the ancient Greeks did not completely own the word. They used a root from the Semitic language - brq. It is translated as “to shine.” The English version of the name for emerald, emerald, also appeared thanks to the Greek. But this word came to Europe from vulgar Latin (common) - Esmaraldus. In ancient French the term was written as Esmeraude. In Middle English it became Emeraude, modified over time and got the form we have now. By the way, the name Esmeralda is translated as a green gem or emerald. |
| Morphology | The natural formation of emeralds occurs due to the interaction of felsic magma with rocks that host ultramafic igneous rocks. Therefore, the natural place of formation of emeralds is represented by zones with high or medium-temperature leaching - greisenization. Rarely, there are cases of emerald formation due to exocontacts of pegmatites. But it is worth considering that then the stones come in small sizes. It is believed that the best quality emeralds come from hydrothermal veins located in carbonaceous shales. |
Emerald is a gemstone from the beryl group of the first order and is equal in value to diamond, sapphire, ruby, chrysoberyl, alexandrite, noble spinel and euclase. The quality of a mineral is determined by its color characteristics and degree of transparency. An ideal specimen should be absolutely transparent with a uniform, rich color. A large, flawless, brightly colored emerald weighing over 5 carats is valued even more expensive than a diamond.
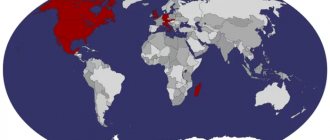
Emerald deposits
High-quality emeralds are rare and are mined in countries such as Colombia, New Granada, Zambia, Brazil and Egypt.
Low quality samples are common in Austria, Ireland, and Norway. — Advertising —
In addition, Russia, USA, Canada, Australia, Spain, France, Switzerland, Italy, Germany, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, China, Cambodia, Ethiopia, South Africa, Somalia, Nigeria, Namibia, Tanzania are well known among emerald suppliers. , Zimbabwe, Mozambique and Madagascar.
Emerald
There is no color that would be more pleasing to the eye than the color of emerald. For we also look with pleasure at green grass and tree leaves, and at the emerald all the more willingly because in comparison with it no thing is greener. Moreover, they only satisfy the eyes, but do not oversaturate... They do not change either in the sun, or in the shade, or under lamps, and are always excellent and brilliant...
People have long had a special affection for green stone. It has been noticed that the passion for it most often began after bloody wars. It was then, when peoples were tired of fierce battles and battles, that the screaming ruby - a symbol of blood, violence and passion - was replaced by the calm cheerfulness of the green stone, promising long-awaited peace and permanence.
Among green gems, the brightest, noblest and rarest is emerald, or, as the ancient Greeks called it, emerald. Its best crystals were valued more than diamonds. According to the classification of A.E. Fersman, emerald belongs to semiprecious stones of the first order, which, as is known, also includes diamond, sapphire, ruby, chrysoberyl, alexandrite, noble spinel and euclase.
Mineralogists call emerald a variety of beryl colored with chromium oxide in a grass-green color. Brownish, opaque beryl has an unattractive appearance. But its transparent crystals are wonderful. These are color-changing aquamarine, and golden-yellow heliodor, and soft pink sparrow... But the most beautiful in this family of gems is emerald.
Emerald is a high-class gemstone. Large, uncracked, bright green emeralds cost tens of thousands of dollars per carat (more expensive than diamonds of equal size). Emeralds are rarely flawless. Its precious varieties are often characterized by the presence of a complex network of thin veins and cracks that dissect the stone. Sometimes emerald contains small inclusions of well-formed crystals of calcite (Columbia), mica, actinolite, tourmaline (Ural, etc.). High-grade emeralds are found in veins located in carbonate rocks of Colombia (Chivor, Muso, etc. deposits). It is believed that the Incas obtained emeralds from these mines. Ural emeralds (Russia) have also long been famous. Primary deposits of emeralds were known in Ancient Egypt (Cleopatra's mines). Pale colored emeralds come from Brazil.[5]
History of emerald
The term “emerald” has Persian roots, which were transformed into the Latin smaragdus and were then used by many peoples of the world.
Even in ancient times, emeralds were highly valued. In Babylon they were an object of trade as early as 4000 BC. e. Ancient Egypt was famous for its emerald mines, which were discovered in the 19th century along with tools from 1300 BC. e. The rulers of India also valued emeralds. Sultan Shah Jahan, who built the magnificent Taj Mahal, the greatest symbol of love and fidelity, used emeralds as talismans. In addition, they were engraved with sacred texts.
And now, like many centuries ago, emeralds remain one of the most popular gems.
Colors and varieties
The color of emeralds is always green, although it may differ in hue, depth and saturation. Gems are classified according to their place of origin.
Colombian emeralds
Colombia leads in terms of gem production (50-95% of total production). Colombian stones have a deep blue-green color, good transparency and a minimum of defects. Therefore their cost is high. A local curiosity are the Trapiche emeralds, which have a pattern inside in the form of a wheel and six spokes radiating from its center.
Colombian emeralds
Zambian emeralds
Zambia is the second “emerald country” after Colombia. Fewer gems are mined there, but their quality and, accordingly, cost are much higher. Zambian emeralds are perfectly clean and transparent, have a green color, and sometimes a yellowish or bluish tint.
Zambian emeralds
Brazilian emeralds
The local gems are also of high quality and have a minimum of defects, but they are much lighter and larger. It was in Brazil that a valuable specimen weighing 11.5 kilograms was discovered, later named Teodora and valued at $1.15 million.
Emerald Teodora
Egyptian emeralds
Egypt is famous for the antiquity of its deposits. For example, mines near Mount Zabara and near the city of El Quseir were developed back in 1650 BC. e.
Ancient Egypt jewelry with emerald
This is interesting!
The oldest deposit is located near the city of Aswan - it is designated by the Egyptians as “the emerald mines of Queen Cleopatra,” which has long been considered a myth. Today this version is also questioned. The mines date back to the time of Pharaoh Sesostris III (1872-1853 BC). However, it was in them that working tools were found, made, according to archaeologists, around 1300 BC. e.
Afghan emeralds
They are also called Panjshir emeralds, after the name of the gorge where mining is carried out. Afghan emeralds are practically not inferior in quality to their Colombian and Zambian counterparts, but there are much fewer of them on the market, and therefore the cost is higher.
Afghan emeralds
This is interesting!
During the Afghan war, emerald mining there was controlled by the field commander and Minister of Defense of Afghanistan, Ahmad Shah Massoud. The mined stones were sent to Pakistan, where they were processed and then supplied to the world market. The trade in stones at that time brought the country an average of about 10 million dollars a year.
Ural emeralds
In 1831, master stone-cutters Maxim Kozhevnikov and Yakov Kokovin discovered emeralds for the first time at the junction of the Tokovaya and Bolshoi Reft rivers, which is located 90 kilometers from Yekaterinburg. Since then, the field has been actively developed. Mostly opaque specimens of record sizes and a deep green color are found there.
Ural emeralds
Zimbabwean emeralds
Slightly lower quality gems are green, but shimmering yellow.
Zimbabwean emeralds
South African emeralds
In South Africa, light green emeralds are mined, speckled with small cracks and therefore cloudy. They are processed mainly cabochon.
South African emeralds
Record emerald
— Advertising —
The world's largest emerald, originally from Colombia, was named "Fura". Its weight was 11,000 carats and its price was $150 million. The second largest mineral, named “Tena,” weighs 2,000 carats. The record holder for cut stones called “Theodora” weighing 11.5 kg was valued at $1,500,000. Before treatment, his weight was 28 kg.
Origin of stones
Greisen, or emerald ore, is found on all continents. It should be noted that its presence is only a sign of the presence of a precious vein. Emerald inclusions are formed as a result of the action of thermal springs on basic igneous rocks such as granite.
The leaders in emerald mining are the following countries:
- Colombia, producing from 50 to 95% of the world's total. Currently, there are two active fields: Tonghe and Muso. In the latter they find unique specimens called trapiche. These dark-colored crystals have light, radially located zones.
- In recent years, Brazil has come close to becoming the leader in production volumes and quality of emerald crystals. They are lighter and purer than the samples mined in Colombia, but have a lower density. Interestingly, the largest emerald, called Theodore, was found in one of the Brazilian deposits.
- Zambia shares with the previous country the second place in the number of esmeraldas produced per year. Some experts note that they are superior in quality to Colombian samples.
- Egypt. This country is home to one of the oldest emerald deposits in the world. It is located near the city of Aswan. Its active development began about 4 thousand years ago.
- Russia is one of the world leaders in the extraction of natural emeralds and the production of artificial ones. Natural Russian stones have a rich green color.
Physico-chemical characteristics of emerald
Emerald is a type of beryl, a colorless stone that is colored by impurities of certain metals.
Thus, emeralds are characterized by a rich velvety green color, with a blue tint due to the presence of chromium, iron and vanadium in the mineral composition. Emerald crystals have an elongated prismatic shape. They are transparent or translucent, fragile with a glassy sheen, without cleavage, uneven or conchoidal at the edges.
The hardness of emerald on the Mohs scale is 7.5-8.0. The specific gravity is 2.8 g/cm3. Refraction from 1.576 to 1.582.
History of modern emerald
Descriptions of emeralds are found not only in Slavic chronicles, but also in the writings of Ancient Egypt and Rome.
Cleopatra had her own large deposit of gems. The Egyptians believed that the gods gave them the stone. It symbolized spring and eternal youth.
Emerald was highly valued in Babylon and India. The crystal was presented as a gift to high-ranking officials and wealthy people.
To have jewelry with a mineral meant to have magical powers. It was often given to beloved women. It was believed that jewelry decorated with this stone would protect against the evil eye and damage.
Mankind knows many types of emerald. But it was only in the 19th century that people discovered the chemical composition of emerald. Green beryl is given its rich color by chromium or vanadium oxide. Allowed to contain iron impurities.
Magical properties of emerald
The main task of the emerald is to overcome the bad inclinations of its owner: deceit, a tendency to cheat, and infidelity to loved ones.
If the owner of the stone does not have such inclinations, then the emerald will bring him good health and success. And if the gem doesn’t like a person’s behavior, he can even punish him. Emerald reacts especially poorly to aggression and rudeness. Emeralds dispel negative energy, cleanse a person’s aura and his home from everything negative. They are considered the patrons of the family hearth: they maintain peace and harmony between spouses, and have a positive influence on procreation.
Psychics use emeralds to contact the souls of the dead and understand signals from higher powers.
Properties
Valuable mineral rock has a number of characteristics unique to it. There are no maximum or minimum weight limits for emeralds: natural gems can weigh a few milligrams or a kilogram or more. Naturally, after professional cutting the mass becomes smaller, but the stone is also more beautiful.
Physical properties of the mineral:
- The hardness of a gem on the Mohs scale is significantly lower than that of a diamond and amounts to 7.5-8 units.
- Density - about 2.5 g/cm³.
- The chemical composition is identical to beryl. The green, grassy color comes from chromium and vanadium oxides. The exception is black emerald, which contains iron oxide.
- Resistant to acids and alkalis.
- Loses color and decomposes at 700°C.
The healing properties of emerald
Emeralds can stabilize blood pressure, relieve pain in the head and joints, and help in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and bladder inflammation.
They are characterized by a pronounced antibacterial effect. Previously, the stone was used to treat night blindness, cataract, and epilepsy. Modern lithotherapy suggests using the gem to eliminate nightmares, insomnia, groundless fears and increased fatigue.
Industries where emerald is used
The main use of emeralds is their use in jewelry.
Rich dark green samples are considered the most valuable; even if they contain foreign inclusions, they are valued more than pale stones. Emerald inserts decorate jewelry and are kept in museums and private collections. In addition, natural emeralds are used in the manufacture of solid-state lasers, and synthetic stones are used in quantum electronics.
What is an emerald? Properties, extraction, history of the gemstone
Emerald is a 1st class gemstone. Large emeralds , absolutely free from defects, with a rich, dense tone, weighing from 5 carats, are more expensive than diamonds. An emerald is considered ideal in cases where a perfectly transparent stone has an evenly distributed rich color.
The main criterion for the high quality of an emerald is its color, but transparency comes in second place. Stones of natural origin almost always have splits and cracks, and only occasionally are specimens found that are ideal in all respects, and they are very highly valued.
Emeralds come in various colors - from green-yellow to blue-green, but the main color is always green, sometimes even dark green. The color distribution is almost always uneven; very often the base of an emerald crystal is darker in color than its free end.
The word "emerald" comes from the Perso-Arabic zumurrud, as well as from the Turkish zümrüt. Previously, in Russian the word emerald was written as izumrut.
Turkish and Arabic words come from the Greek word σμάραγδος, smáragdos, previously used in the languages of the Slavic peoples, which translated means a green gemstone.
In Europe, emerald has the following names: in Spain it is called esmeralda, in Germany this stone is called emerald, and in France it is called emerald.
Varieties of emerald
Emerald occurs in various species in nature. Brazilian emerald has a transparent green tint. Quite a rare name Trapiche, emeralds of this type have the shape of a carriage wheel with spokes. They are usually found in Colombia.
Another type is called emerald - malachite or eurohit. The next variety of emerald is called Vilyuisk or Vesuvian. There are also copper emerald or dioptase, Ural or demantoid and nickel emeralds.
Physical properties of emerald
According to the well-known classification of A.E. Fersman, the emerald mineral belongs to the first-order semi-precious stones. They also include diamond, ruby, euclase, sapphire, alexandrite, chrysoberyl, and noble spinel.
Emerald is a transparent variety of beryl that has a grassy green color. This color shade is given by vanadium oxide or chromium oxide, very rarely there is an admixture of iron oxide, usually South African emeralds. Emeralds are characterized by increased fragility; their hardness ranges from 7.5-8 units on the Mohs hardness scale.
Diamond, unlike emerald, has a hardness of 10.0. The transverse separation, combined with small, thin cracks that are often found in emeralds, makes this mineral very sensitive to pressure and high temperatures. At 700 degrees and above, emeralds easily lose their color, but they are resistant to various reagents and acids.
Emeralds often have various defects. Precious varieties of emeralds are very often characterized by the presence of a rather complex network of thin cracks and veins that cut the stone lengthwise and crosswise.
Zoned emeralds are also often found , the crystals of which have a longitudinal change in color intensity, usually with a lighter and brighter core, as well as with transverse alternation of dark and light green zones.
In light emeralds, even without magnifying devices, but by eye, dichroism is clearly visible, that is, a change in the color of the mineral from bluish to yellowish-green when the crystal is rotated.
The best emeralds contain approximately 75% tone. In addition, a high-quality emerald should be well saturated with color, its shades should be light and bright. Gray color is normal.
emeralds of the highest standard quality are transparent , but they are often clouded by various inclusions of gas, bubbles and liquid, as well as healed cracks, pinpoint inclusions of other minerals captured by emerald crystals during their growth. It is by the mineral composition of the inclusions contained in an emerald that it is determined from which deposit a given specimen was mined.
Transparency of emerald
Basically, all emeralds contain a large number of inclusions and surface fractures. Unlike a diamond, whose quality is assessed at 10x magnification, an emerald is assessed by eye.
Thus, it turns out that if an emerald does not contain cracks and flaws visible to the eye, of course, provided that visual acuity is good, then it is considered flawless.
Emerald crystals that do not have surface irregularities are quite rare, so almost all emeralds are chemically treated with various mixtures to give them the most pleasant and beautiful appearance.
The irregularity and uneven shape of emerald crystals makes it possible to use the cabochon method instead of simple cutting. The emerald cut , which intensifies color tones, was designed to avoid chipping the corners of the gemstone.
Origin of emerald in nature
Emerald crystals are formed by the interaction of felsic magma with ultramafic host rocks, so their deposits are usually caused by zones of greisenization of ultramafic rocks or phlogopite mica, sometimes emeralds are found in or near pegmatites. However, the best quality emeralds are found in hydrothermal veins that lie in carbonaceous shales.
Alluvial placers of emerald crystals practically do not form, due to the fact that emerald is close in density to quartz. Secondary deposits are caused only by weathering crusts.
As a result of greisenization processes, in the presence of feldspars and granites, light-colored micas are formed. Such as muscovite or lepidolite.
As a result of this process, the original rocks turn into greisen, which are complex rocks containing light micas and quartz.
Very often, greisen are saturated with valuable ores and minerals in the form of small inclusions. The choice for deposit development is made, as a rule, in the presence of greisens containing ores of rare colored stones and rare metals.
The process of greisenization is necessary for the formation of emeralds . In most deposits discovered on earth, the formation of emerald is confined to the presence of phlogopite mica; they are usually formed as a result of the interaction of ultramafic rocks and high-temperature water solutions.
In Colombia, emerald crystals are found in low-temperature carbonate veins that are adjacent to black bituminous limestones. Quite rarely, small emeralds are formed in exocontacts of various pegmatites.
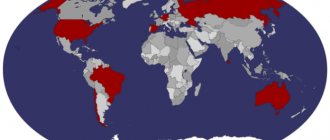
Emerald deposits
Colombia is considered the largest and richest emerald deposit In recent years, 95% of all emeralds are mined there. From 2000 to 2010, emerald mining in Colombia increased by 80%. Also, deposits of this mineral are located in Zambia in the vicinity of the city of Kitwe.
In 2004, approximately 20% of all emeralds in the world were mined from this deposit, such statistics placed Zambia in second place after Colombia in emerald production. During the first half of 2011, 3.7 tons of emeralds were mined from the Kagem deposit.
Emeralds mined in Zambia are considered better than those from Colombia, as they are of high and impeccable quality. Emerald deposits are also found in these countries: Austria, Afghanistan, Australia, Bulgaria, Brazil, China, Cambodia, Canada, Ethiopia, Egypt, Germany, France, Kazakhstan, India, Italy, Namibia, Madagascar, Nigeria, Mozambique, Norway, Russia, Pakistan, Somalia, Spain, South Africa, USA, Switzerland, Zimbabwe and Tanzania.
High quality emeralds are quite rare. Most of them are found in several deposits: on the Red Sea coast, in the Zabara mountains near the city of Kosseir in Egypt, there is a deposit that, according to hieroglyphic inscriptions discovered there, was developed in 1650 BC; an emerald deposit called Tunja was discovered in 1555 in Colombia; Another famous deposit is located in the town of Muso, in New Granada, which has been developed since 1537.
Emeralds of significantly lower quality are mined in Norway, near Lake Mjosen and in its environs, in Ireland in the town of Mourn, in Habachtal, in Salzburg, Austria. In the Russian Federation, emerald crystals are found 90 km away. northeast of Yekaterinburg on the Tokovaya River.
There is black mica slate there. Emerald deposits are also known at the sources of the Bolshaya Refta River. The stones mined in these places are famous for their size. The Bolshaya Refta River is also rich in phenacite and alexandrite.
Under Pharaoh Sesostris III, who reigned about 37 centuries ago, emerald deposits were developed, which gave the world many beautiful specimens. They are located near Aswan, 50-65 km. from the Red Sea.
Slaves dug mines in hard rocks, the depth of which reached 200 meters. One such mine could house about 400 people at a time. They believed that emerald did not like light, so all work was carried out in absolute darkness.
The emerald-bearing rock was removed to the surface, then chopped into pieces and generously smeared with olive oil, this helped to distinguish and select precious minerals, which the ancient Romans and Greeks called stones of green radiance.
History of emeralds
In ancient times, emeralds were highly valued by the rulers of India. It is believed that the builder of the Taj Mahal, the famous Sultan Shah Yahan, wore emeralds as a talisman, they were depicted with sacred scriptures.
Most likely, it was because of this that emerald was credited with influencing love, because the Taj Mahal is one of the greatest symbols of devotion and love.
The famous report of Juan de Samano, who was the secretary of the great Emperor Charles V, indicates that Colombian emeralds were first found in 1525. And this was associated with the first expedition of Diego de Almagro and Francisco Pizarro.
This mineral was also highly valued by ancient cultures. The inhabitants of Babylon sold emeralds back in 4000 BC. The famous emerald deposits belonging to Cleopatra were located in the vicinity of Aswan in Egypt.
For many years it was believed that these deposits were just a fictitious story or legend, but in 1818 they were discovered again in these places. And in the old mines, tools were found that were later definitely dated back to 1300 BC.
By 1530, almost all emerald deposits and mines were known to Europeans. Their number was not large. After the Spanish conquest of Colombia, large quantities of emeralds found their way to Europe.
In ancient Egypt, there was a Book of the Dead, in which it was written that the Egyptians accepted an emerald as a gift from the great god and ruler Thoth. Green color speaks of spring and therefore emerald was considered a symbol of eternal youth.
The peoples of Egypt called this mineral the stone of the goddess Isis. And they endowed him with the ability to turn dreams into reality, see the past, read minds and predict the future.
It was also assumed that emerald is capable of rewarding a person with unchanging love and loyalty. He was considered the patron saint of expectant mothers, and the emerald was the best gift for a pregnant woman. Emeralds were also very popular in ancient Egyptian jewelry.
And a huge number of people wanted jewelry with emeralds to be placed in their tombs after their death. There is a legend about the great emperor Nero, which says that he had a large emerald, which he used as a monocle when he watched gladiator battles.
Artificial emerald
Since the 19th century, scientists from many countries have been involved in the task of creating artificial emeralds.
For the first time this was possible only in 1935 in Germany, when G. Espig and his colleagues obtained the so-called “igmerald”. 5 years later, industrial production of the synthetic mineral was established in the USA. Today, artificial emeralds are produced in countries such as Germany, France, Switzerland, Japan, Russia and Belarus. The world's largest (a joint enterprise between Russia and Thailand) synthesizes emeralds that are identical in chemical composition to natural Colombian ones. Synthetic emeralds often reach large sizes up to hundreds of carats, but the technology for their production remains a secret of the enterprises and is not disclosed.
In general, modern synthetic emeralds are no different in appearance from natural ones, and the quality is even higher. Moreover, their price is much lower than natural stones, which are quite rare.
Hydrothermal emerald (artificial)
Emeralds grown by hydrothermal and solution-melt methods. This type of emerald is grown in a special laboratory. Such stones in their qualities - including jewelry - do not differ from natural emeralds grown in the thickness of the earth's crust.
Artificial emerald is grown from emerald powder dissolved in water using high temperature. That's why it's called hydrothermal. A solution of water, ground emeralds and special chemicals enters a cold zone, where the emerald is deposited onto a special substrate - a seed. The result will be a mineral with the desired properties. The interesting thing is that the growth process of the gem can be controlled. To do this, it is necessary to select the required position and size of the seed. On average, the cultivation of hydrothermal emerald lasts about a month. The ability to create artificial emeralds makes them more accessible to gemstone lovers. Moreover, as already mentioned, emeralds grown in this way are not inferior in quality to real ones.
How to distinguish an artificial emerald from a natural one
Artificial emerald is very similar to natural stone, but its specific gravity and refractive index are lower. In addition, it is characterized by a bluish-green tint. In the Chelsea filter it looks bright red. It is also possible to distinguish between natural and synthetic emeralds using ultraviolet radiation (wavelength 360 nm), a real stone does not react to it, but a synthetic one luminesces in a chestnut-brown color. But this pattern may not be observed.
How to distinguish an original from a fake
Uncut emerald
Under the guise of emeralds, ennobled, cheaper gems such as chrysoberyl, zircon, verdelite, tourmaline and others, or even ordinary glass, can be sold. To identify a fake, you need to evaluate the following parameters of the stone:
- Color. It should be green, it can be muted, have a yellowish or bluish tint, but the main color is still green. Swamp-colored or bottle-colored gems are not emeralds; most likely, they are beryls.
- Dichroism. It is always present in emeralds, which appear blue or gold when the stone is viewed from different angles.
- Clarity of edges. Smooth corners indicate a fake.
- Uniformity and perfect structure. Natural emeralds are homogeneous, that is, they do not have layers. At the same time, internal perfection may indicate synthetics; in nature, samples without cracks, air bubbles and small inclusions are extremely rare.
- Color preservation. If you place a natural pebble in water or hold it under the sun, its color will not change, while imitations may become darker or lighter.
There is another type of fake emerald on the market - the doublet. This is when only the thinnest plate glued on top of cheap material is natural in the stone. Such deception can be detected by carefully examining the side edges of the sample.
It is very difficult to distinguish artificial emeralds by eye; their ideality can serve as a guide. Professionals identify synthetics by their ability to luminesce in ultraviolet rays, while natural emerald does not react to them in any way. Although there are exceptions to this rule. Also, artificial emeralds, when viewed through a Chelsea filter, give an intense red tint.
Emerald and zodiac sign
Emeralds are recommended for nervous people with increased sensitivity; it helps them avoid stress and exposes scammers and deceivers.
The gem is well suited for Leo, Libra and Aquarius. Emerald is absolutely not recommended for Pisces, Capricorns and Scorpios. Representatives of other zodiac signs can wear jewelry with it without any worries.
Emerald stone: who suits it according to their zodiac sign
The planet that controls the magical properties of the mineral is the Moon.
The period of highest activation of healing and magical powers: June 22 – July 22.
Incompatibility with the gem is observed in Capricorns.
For other signs of the Zodiac, emerald can bring undoubted benefits and become a reliable amulet, especially for Cancer, Pisces, Taurus, Sagittarius and Gemini.
Cancer. For him, this mineral is among the most important stones. Its radiance will melt hidden fears, suspiciousness and help you gain confidence in important endeavors. An emerald for Cancer should be framed in silver: this is the most successful precious combination for the emotional and vulnerable nature of this sign. Such an emerald talisman will give balance, bring cheerful colors, and cure melancholy.
Twins. The expressive essence of Gemini will be pacified by the energy of the dark emerald. This is where the magical qualities of the stone come in handy: Gemini needs composure and wisdom. At the same time, it will eliminate nervousness and relieve self-reflection. Like Cancer, Gemini should choose silver jewelry with a mineral, preferably pendants.
Calf. This sign should choose a gem of a grassy shade. It will add optimism and bright events. Like a stone that attracts luck, the green emerald will push Taurus to success, which a stubborn person can wait for years.
Sagittarius. An ambitious nature born under this constellation will be favored by a large stone. The psychological magic of emerald will work here: failures of any kind will seem like an everyday trifle that can be easily overcome. It will also help strengthen Sagittarius’ influence on loved ones and subordinates.
Fish. The gem brings success and joy from life to this sign of the water element. He will teach you to enjoy every day to the fullest and control your weaknesses.
Just like in ancient times, emerald today is one of the most beloved precious stones. The largest private collections of it are kept in the Middle East.
National treasures are collected in major museums around the world. Modern rulers, elite circles, and show business stars are trying to comprehend the magical magic of the stone.
The largest jewelry houses and designers create luxurious items with gemstones worthy of crowned heads.
Prices for emerald products
Low-quality emerald prices start at $350 per carat, while high-quality stones start at $8,500 per carat, which is influenced by the color, clarity and origin of the stone. As the weight of a gem increases, its value also increases. Thus, specimens with rich color and weight of 5 carats are valued at $15,000 per carat.
How to choose an emerald and how to distinguish a fake?
Large emeralds of high quality are very rare and cost more than a diamond of the same weight. When purchasing a stone for further setting into jewelry, you should be careful, because the gem may have defects that are invisible to the buyer, but can split the mineral when setting. Depending on the deposit, emeralds may have a yellow or blue tint - this is considered normal for stones.
So, how to distinguish a fake from a natural stone:
- Color. Natural emeralds have an intense, rich green color. A light-colored gemstone can be very similar to an emerald, but it is often a simple beryl rather than an emerald. A large number of cheap Chinese brands, sold in Russia under Russian names, sell simple beryls under the guise of emeralds. So again, natural emerald is dark green in color. Not light green. Not light green. And certainly not gray.
- The presence of cracks and inclusions in the stone. Natural emerald is a fairly strong stone, so minerals that have cracks on the surface should be taken with great care. Small inclusions in the gem are quite acceptable. The formation of emerald takes place in turbulent conditions, so foreign solids, liquids, and gases can penetrate into the mineral. Inclusions make the mineral unique, which is why an emerald with beautiful inclusions is more valuable than a stone with an even color.
- Gem defects. A magnifying glass will help you distinguish the imperfections of the mineral, as well as its cuts, which are inaccessible to the naked eye.
- Transparency of the stone. A high quality natural gemstone may contain clouds of inclusions, but it should be largely transparent.