Jewelry products have their own specifics in the field of mandatory labeling . to such a product , and applying an identification code directly to the product requires special equipment.
In this article we will tell you which jewelry items are subject to mandatory labeling , what equipment will be needed when working with this group of products , and by what time market participants need to prepare.
Dates for introducing jewelry labeling
The government planned to make labeling of jewelry mandatory 2021 . It was assumed that from January 1 there would be a ban on the import and production of jewelry without the possibility of identification. And they wanted to ban the sale of unlabeled products from July 1. However, representatives of small businesses did not have time to prepare and the deadline was changed.
On March 1, 2021, marking of jewelry was launched . Companies could take part in the experiment voluntarily. It was enough to register in the GIIS DMDK and register for special registration with the Federal Assay Office.
On April 1 , 2021, market participants were allowed to try out technological solutions for applying identifying marks directly to products .
From March 1, 2022, labeling of jewelry will become mandatory and will take place in the planned two stages. The presence of DataMatrix code will become mandatory for imports and manufacturers. Participants in the turnover will enter all transactions carried out with jewelry into the GIIS DMDK system, namely:
- put products into circulation;
- transfer ownership rights;
- send and move goods to warehouses or points of sale;
- remove products from circulation after sale to the final consumer.
From March 1, 2023, the import and sale of jewelry without a physical mark will be prohibited, but storing unmarked products in a warehouse will be permissible.
From March 1, 2024, it will be prohibited to sell and store jewelry without identification marks.
Testing and hallmarking of jewelry made of precious metals
In the Russian Federation, jewelry and other products made of precious metals that go on sale are subject to testing and stamping with the state hallmark (Article 12.1, 41-FZ).
Jewelry can be domestically produced, as well as imported into the territory of the Russian Federation from countries that are not members of the Eurasian Economic Union, and moved into the territory of the Russian Federation from countries that are members of the Eurasian Economic Union.
Jewelry made of precious metals without an imprint (Article 12.1, 41-FZ) of the state hallmark may be on sale in the following cases:
- if these are domestically produced silver products, the hallmarking of which is carried out on a voluntary basis;
- if these are watch industry products imported into the Russian Federation and bearing imprints of the official mark of the Swiss Confederation.
Testing, analysis and hallmarking of jewelry and other products made of precious metals is carried out by territorial bodies (Order of the Ministry of Finance 47n) (divisions of territorial bodies) of the Federal Assay Chamber.
The territorial body (divisions of territorial bodies) of the Federal Assay Chamber affixing an impression of the state hallmark on products made of precious metals:
- guarantees that it has verified the precious metal content of products made from precious metals;
- confirms the compliance of the actual sample with the sample specified in the imprint of the legally established sample standard;
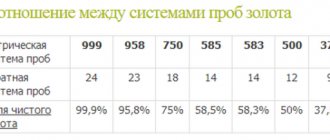
The following standards are established for jewelry in Russia (PP 394):
- gold - 375, 500, 583, 585, 750, 875, 916, 958, 999
- silver —800, 830, 875, 925, 960, 999
- platinum - 585, 850, 900, 950
- palladium - 500, 850
Products made from gold alloys below 375 standard, as well as silver products below 800 standard, platinum products below 585 standard, palladium products below 500 standard are not jewelry (41-FZ) and are not subject to state hallmarking, cannot be sold as jewelry and other products made of precious metal (the state does not guarantee the content of precious metals in them).
Jewelry made from 583-karat gold can be made upon orders from individuals only from 583-karat gold products that they own. Jewelry of 583 hallmark was made earlier, however, products of this standard are in use by individuals and if it is necessary to repair or manufacture a new piece of jewelry from an existing alloy of gold of 583 hallmark, branding with 583 hallmark will be carried out.
State hallmark is a sign of state control carried out in the interests of the buyer over the compliance of the content of precious metals in jewelry and other products with one of the hallmarks established in the Russian Federation and imposed on such products as a state monopoly.
The presence of an imprint of the state hallmark on a product means that the product has a hallmark no lower than that indicated in the stamp.
The hallmark can be main or additional
The main mark includes the following elements:
- the identification mark is a sign of nationality of the hallmark, currently it is a female head in a kokoshnik in profile, turned to the right;
- code of the territorial body (division of the territorial body) of the Federal Assay Office, which hallmarked the product;
- a hallmark indicating the number of parts by mass of the precious metal in a thousand parts by mass of the alloy.
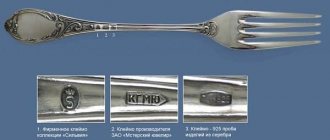
An example of the main hallmarks for branding products made of gold, silver, platinum and palladium
| in the form of a spatula for branding gold items |
| in the form of a rectangle with convex opposite horizontal sides for hallmarking silver products |
| in the form of a rectangle with cut corners for branding platinum products |
| truncated oval shape for stamping palladium products |
An additional mark contains a hallmark. An additional hallmark is used when hallmarking jewelry and other products in combination with one of the hallmarks. An additional hallmark may have an independent meaning when marking:
- products that have an area insufficient in size to affix the main hallmark letter B or the identification mark letter A in combination with an additional hallmark letter D;
- parts of jewelry and other products that are secondary and (or) additional for their intended purpose.
An example of additional stamps for branding products made of gold, silver, platinum and palladium
| in the form of a rectangle for branding gold products |
| in the form of a rectangle with convex opposite horizontal sides for hallmarking silver products |
| in the form of a rectangle with cut corners for branding platinum products |
| in the form of a circle for marking palladium products |
By what methods can an imprint be made on jewelry?
- Mechanical: the stamp imprint is applied to the product by impact using a special tool using stamping machines.
- Laser: the stamp imprint is applied using a laser machine using a stamp mask or using a scanner method.
- Electro-spark: the stamp imprint is applied by a spark discharge using a brand electrode and a stamping machine. The electrospark method of affixing the state hallmark is being withdrawn from use and is being replaced by a more progressive method - the laser method.
The choice of branding method is carried out by the territorial body (division of the territorial body) of the Federal Assay Office and depends on the degree of readiness of the product, technological features, etc.
A little history: chronology of hallmarks
On January 1, 1899, a standard stamp was introduced for branding gold and silver items, the elements of which were an identification mark in the form of a female head in a kokoshnik, turned to the left; the initials of the manager of the assay district and a sample indicating the number of precious metal spools in the alloy.
Since 1908, the elements of the mark have been: an identification sign in the form of a female head in a kokoshnik, turned to the right; code of the assay district and sample indicating the number of precious metal spools in the alloy.
On June 1, 1958, the elements of the mark are: an identification badge with the hammer and sickle emblem against the background of a five-pointed star; inspection code and sample size specified in the metric system.
Since 1994, hallmarks have been introduced and are currently in effect. The elements of the mark are: an identification sign in the form of a female head in a kokoshnik, turned to the right; inspection code and sample size specified in the metric system.
How does jewelry labeling work in 2021?
With the help of mandatory labeling, you can track the entire path of products from the manufacturer to the end consumer. A special identification code allows you to obtain information about the movement of jewelry goods in several stages.
For jewelry, marking code is provided not by the Center for the Development of Advanced Technologies, but by Goznak. Accordingly, participants in turnover use the GIIS DMDK system instead of “ Honest ZNAK ”.
The procedure for working with marked goods is as follows:
- suppliers and importers order markings from Goznak;
- the provided identification codes are applied to jewelry and special tags;
- participants in turnover register warehouse movements and transfer of property rights in the GIIS DMDK ;
- When selling to the final buyer, the seller scans the code at the checkout. After this operation, the product and identification code go out of circulation.
These measures will eliminate the sale of counterfeit and low-quality goods and fair among entrepreneurs .
Which jewelry items are subject to labeling?
Gold , precious stones should be marked , namely:
- gold and platinum jewelry ;
- gold coins ;
- cut and rough diamonds;
- diamonds, sapphires, emeralds and rubies;
- platinum and palladium powder.
Silver and silver goods , as well as products whose weight does not exceed three grams, are exempt from mandatory marking
Marking order
Unlike other goods, the labeling of jewelry is controlled not by the CRPT, but by Goznak. Therefore, participants in the turnover of jewelry products will work with the GIIS DMDK system. Goznak will also provide unique years of marking.
GIIS DMDK - State integrated information system in the field of control over the circulation of precious metals and precious stones.
What the jewelry labeling process will look like in general:
1
The manufacturer or importer orders a code for each product from Goznak, applies the received code in the form of a label on the tag and marks on the product itself.
2
When the finished product is transferred to the distributor, the code is read, and all information about the movement of goods is transferred to the GIIS DMDK.
3
During retail sales, the cashier also scans the marking code, information about this is automatically sent to the GIIS DMDK, and the jewelry is excluded from circulation.
Gold, precious stones, precious metals, as well as products made from them are subject to marking:
- diamonds (including rough);
- rubies;
- diamonds;
- sapphires;
- emeralds;
- platinum and palladium powder;
- Golden coins;
- gold and platinum jewelry.
Marking of silver and silver products has not yet been introduced. The mandatory labeling requirement also does not apply to products weighing up to 3 grams.
What is GIIS DMDK and how does it work
GIIS DMDK is a state information system (GIS) that controls the circulation of precious metals and precious stones and jewelry . Participants in this market interact in GIS with each other and with government regulatory authorities.
GIIS DMDK contains information about jewelry , their description and identification codes. If necessary, the system can generate a statistical or reference report or obtain a reconciliation report upon request.
To interact, you need to register in your personal account at GIIS DMDK . rule and user manual can be viewed on the official website of the system in the “How to connect” section.
What you need to work with jewelry labeling in 2021
The process of preparing work with marking consists of several steps:
- Purchase of an electronic digital signature ( EDS) with an enhanced qualified security key certificate.
- Ordering and receiving a certificate of no debt from the tax service.
- Registration of a personal account on the GIIS DMDK website.
- Preparing the necessary equipment:
- cash registers with software adapted for labeling ;
- scanners for reading marking codes;
- printer for printing labels.
- Joining the Association of Automatic Identification UNISKAN/GS1 RUS.
- Conclusion of an agreement with Goznak for the provision of DataMatrix codes.
buy an enhanced qualified digital signature only at a certification center accredited by the Ministry of Digital Development of the Russian Federation. TC "Kaluga Astral" is included in the list of accredited organizations and has all the necessary licenses to issue the "GIIS DMDK" for the products "Astral-ET" and "1C-ETP". These signatures make electronic documents legally significant and allow you to interact with counterparties and government agencies.
What should the brand and name tag be?
The state assay mark is a special imprint that is applied by the state inspectorates of the assay supervision of the Russian Federation. It means that the product has been inspected by the inspectorate and has a grade not lower than that indicated in the stamp.
The state hallmark consists of an identification mark and an assay mark , which can be affixed together (in one image) or separately.
Since 1958, the ID badge has been an image of a hammer and sickle against the background of a five-pointed star. This sign is still in use today. Since 1994, an identification sign has been installed, representing a female head in a kokoshnik turned to the right in profile.
The hallmark is numbers showing the number of weight units of the precious metal in a thousand weight units of the alloy. If you see 925 purity, it means that there is 0.925 grams of pure silver per gram of the item.
The hallmark guarantees that the product has passed the test, and the content of precious metal in the alloy is not lower than the declared standard.
Labeling work at different stages of circulation
Participants in the jewelry and precious metals market perform various actions with markings characteristic of the type of activity of the enterprise.
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Mining companies:
- form production batches;
- send a request to Goznak, receive codes and label each package;
- labeled raw materials are shipped.
Raw materials are shipped to refineries , enterprises with which a toll agreement has been concluded, or to product . In the latter case, property rights are transferred.
Manufacturers:
- receive finished raw materials;
- create blanks for the production of jewelry ;
- send them to the Federal Assay Office (FAP) to identify compliance;
- produce jewelry ;
- send finished goods to the FPP for approval;
- order markings and apply them to labels.
When registering a product in GIIS DMDK, they provide information about the batch of raw materials from which the product .
Jewelry processors and manufacturers :
- receive the marked goods;
- manufacture products in compliance with requirements;
- send it to identify correspondence in the FPP;
- order labeling for each unit of goods;
- place markings on tags and packages.
Refineries : _
- purify precious metal from impurities;
- The received products are sent to the owner.
The owner confirms the fact of practical receipt in the GIIS DMDK.
Wholesale customers:
- register the fact of receipt of products ;
- distribute goods to retail outlets.
Retail Stores:
- accept finished labeled products into the jewelry store;
- record the transfer of ownership rights in the GIS;
- remove the product from circulation by scanning the markings at the checkout when selling to the end consumer.
The online cash register sends information about the sale to the fiscal data operator. From there, the data is transferred to the information system for accounting for precious metals and stones .
You can purchase online cash registers, printers, 2D scanners, label printers and other additional equipment for working with labeled goods in our online store. In addition, the buyer will find in the catalog ready-made solutions for his business and technical support services.
Pawnshops
Submit an application to receive DataMatrix codes and, upon receipt, mark the products .
How to mark jewelry
Two hallmarks are applied to jewelry The first is fineness, which means the amount of base noble metal content. The second is a print with encoded information about the manufacturer, the date of manufacture of the product and the territorial inspection to which the manufacturer belongs.
On March 1 , 2022, jewelry products will be marked with an additional tag with a Data Matrix code and identification number.
And from March 1, 2023, the Data Matrix code will look like a nanotag. The new imprint will be placed on each individual piece and precious insert of the jewelry and will not be visible to the buyer. The size of such a mark will be 0.8 mm2. Entrepreneurs are freed from purchasing expensive equipment. Responsibility for applying nanoengraving rests with the FPP. The department will put marks on jewelry along with the hallmark.
Where to apply marking codes
Typically, jewelry contains two imprints:
sample
— it encodes information about the composition and volume of the precious metal
"name"
- it contains information about the manufacturer
Now two more identifiers will be added to them:
from March 1, 2022 - tag
or
a book tag
with a unique identification number and Data Matrix barcode
from March 1, 2023 - nanoengraving
in the form of a Data Matrix, which will be laser applied to each component of the jewelry and to all precious inserts.
The nanomark will be applied by the Federal Assay Office (FAP) along with the sample. The engraving is invisible to the human eye, its size will be 0.8x0.8 mm.
Using a special application on a smartphone, the buyer will be able to scan the barcode on the tag and receive detailed information about the product.
Deadlines for marking leftover jewelry
Precious metals market participants will carry out operations to mark the remaining jewelry as follows:
- Until January 15, 2022, the balances of jewelry products as of January 1, 2022 will be entered into
- By April 1 , 2022, they will conduct an inventory count and update information on balances as of March 31, 21.
- By September 1, 2022, label all declared balances.
From March 1, 2023, the sale of jewelry without nanomarks will be prohibited. And with
On March 1, 2024, the remainder without appropriate marking will be prohibited from being stored in warehouses.
To interact with counterparties, we suggest using “Astral.EDO” and “1C-EDO”. These services allow you to send electronic documents to partners and regulatory authorities, complying with the law.