Among the methods of assay analysis there are: droplet, muffle, chemical-analytical, touchstone analysis. Most often, when determining a sample, the drip method is used (consists of applying a special assay reagent to the test sample) and analysis on a touchstone (features are applied to the stone with a product and an assay needle, after which they are moistened with the reagent and the color of both features is compared to determine the sample). The sample is also determined by an electronic detector using non-destructive testing.
Stages of gold testing
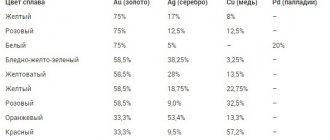
Each product made of precious metal that is imported or sold through retail chains is subject to testing. The process is controlled by the government Assay Office. The jewelry is stamped with a mark that indicates the percentage of gold in the alloy. For example, 750 standard indicates that the noble metal contains 75%, 585 standard indicates 58.5%, etc. For convenience and systematization of branding, state sample systems have been developed, the most famous of which are metric and carat. The latter is used in Western countries.
The process of testing gold products consists of several stages.
- Visual inspection of the product. Particular attention is paid to the quality of the mark, its clarity, evenness of lines and legibility. On fakes, the sample has an uneven structure, numbers and letters are difficult to see. In addition, careful examination of the symbols will help identify gilding or jewelry. A specialist, upon visual inspection of the jewelry, can easily determine its quality and whether it belongs to a particular group of alloys.
- Cleaning the product. With the permission of the owner, part of the surface of the jewelry is cleaned before testing. This is necessary to confirm that the item being tested is truly gold and not gilded. During work, needle files, finely cut files and a tool for precise processing of the surfaces of metal products - a scraper - are used. The procedure is performed from the inside of the product, as carefully as possible and away from the assay mark.
- Application of the reagent. After preliminary determination of the sample, a reagent is applied to the stripped part of the decoration in a vertical position. The drop should not spread. An important point is the exposure time of the assay material on the surface. It varies depending on the type of reagent and sample. Acids on metal with marks 375, 500 and 585 are kept for 5-10 s, and with mark 750 - 20 s. Gold chloride should be on the surface for 7-12 s, potassium iodide - no more than 5 s. Failure to comply with the time intervals will lead to distortion of the characteristic chemical reaction. At the end of the procedure, a drop of the reagent is removed with a napkin or piece of calico.
Applying a reagent to gold
Testing jewelry is accompanied by characteristic reactions, according to which the alloy sample is determined. The procedure is relevant for products on which the mark has worn off and is difficult to see.
How to get colored gold
The most traditional shades of gold are red, white and yellow. However, there are many more metal colors.
Red gold
For a long time, this metal was used to gild domes and other architectural elements, and only then they began to make jewelry from it. Most of the modern jewelry assortment is made in red gold. Copper gives this shade to the metal. The more of it there is in the alloy, the richer the color will be.
Red gold is used in a wide variety of jewelry; it goes well with any inserts, looks elegant and self-sufficient.
Yellow gold
These same alloy components, taken in a different ratio, give the metal a bright yellow or lemon tint. With equal proportions of copper and silver, the metal acquires the best casting properties.
Engagement and wedding rings, jewelry with colored precious and semi-precious inserts are made from yellow gold. Products made from this metal are brighter and more expressive.
White gold
White gold has been no less popular in recent years. Some people believe that the light color is achieved by increasing the proportion of silver in the alloy, but this is not so. To obtain a noble shade, one of the white metals, for example, platinum or palladium, is added to the alloy. These components give the metal not only an exquisite color, but also high strength. The alloy differs from platinum in its light yellowish tint.
Products made in white gold look elegant and respectable. Increasingly, this metal is used for setting diamonds and other cool-toned gemstones.
Brown gold
The metal acquires a beautiful chocolate shade by chemically treating a gold-containing alloy with copper.
Green gold
Oddly enough, silver gives gold its olive-green hue, and to achieve a more saturated emerald color, cadmium is added to the alloy.
In our country, green gold is not traditional. Sometimes floral elements of jewelry compositions are made from it, but still more often an enamel coating is used for this.
Blue gold
Getting a blue or light blue shade of gold is the most secretive. Jewelers do not disclose not only the technology for obtaining the metal, but even the components of the alloy. Experts suggest that the secret of the color transformation lies in the impurities of cobalt or iron. This is a rare case of a two-component alloy.
purple gold
Jewelers call this gold amethyst for its special decorative shade. Most often, aluminum is added to the alloy to achieve the beautiful purple color of the metal. Interestingly, this shade is only possible in an alloy with 750 gold.
Black gold
It turns out that black gold is not only a metaphorical name for oil, but also a real precious metal. There are several known ways to obtain black gold. The first method is to add cobalt and chromium to the alloy and oxidize the metal at high temperature. Also, an unusual shade is achieved by coating red gold with rhodium.
The color of gold can depend not only on the components of the alloy, but also on various chemical influences. Unusual shades are achieved by applying various decorative coatings to metal, as well as as a result of thermal or chemical treatment.
Fashion trends
Combined gold continues to be one of the leading trends in jewelry fashion. Jewelry that combines red and white metal is especially relevant. These alloys are distinguished by their high strength and resistance to external influences, which is why they are used to make jewelry that will delight its owner for many years.
Modern brands create various products from combined gold: with and without inserts, simple and extravagant. Often diamond edges are applied to such jewelry, making the metal more textured.
This season, decorative elements of gold of different shades are combined into something harmonious, making the design of the jewelry more complex.
Types of reagents and their effect on gold alloys
Testing of gold jewelry is carried out using several types of reagents. Each of them is used for a specific alloy and has a characteristic effect on it.
Chlorine gold
Gold chloride is a reagent used for testing jewelry without specifying samples. Thus, you can find out whether the alloy being tested contains precious metal and in what quantity.
Gold chloride is suitable for detecting counterfeits. With its help you can distinguish real gold from gilding and costume jewelry. In addition, the reagent is applicable for white precious metal 500, 583/585.
When choosing a chemical for testing jewelry, you need to know that it only works on alloys with a gold content of up to 60%.
Acidic reagents
Acid compounds for testing precious metals are a mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acids in various proportions. Distilled water is added to them. For example:
- nitric acid density 1.5;
- hydrochloric acid, density 1.20;
- distilled water.
The amount of reagents directly depends on the samples of the alloys being studied.
The effect of acid reagents on gold is of two types. On some products they leave a light stain, on others they do not have any reaction. The chemical element does not affect high-grade alloys or leaves dark marks on them.
Each acid reagent corresponds to a specific sample for analysis: 375, 750, etc. The lower the gold content in the alloy, the more pronounced the color of the reagent stain.
Acidic reagents for gold determination
When testing gold alloys of 375, 500, 750 standard, acid-containing preparations leave a transparent drop on the cleaned area without any trace. In rare cases, a subtle light shadow appears.
If the reagent is dropped onto a product made of base metal, a certain reaction will begin on its surface, followed by bubbling and the appearance of a greenish precipitate. A specific unpleasant odor will also appear.
Potassium iodide solution
The product is used to test alloys with a high content of precious metals. This chemical is used to detect counterfeit metals that are resistant to other reagents. The reagent with a solution of potassium iodide does not work on alloys whose fineness starts from 900. On a product with a mark of 800 and on jewelry with high chemical resistance, a black or green spot will form with possible subsequent bubbling.
How can you dissolve gold?
For many years, chemists used only a dangerous method in which, at extremely high temperatures, gold dissolves in a reaction with fluorine. But in the modern world, new, safer methods are being used.
Amalgam
Amalgam is an alloy of mercury in a liquid or solid state and is used as an industrial refining method. The process of gold amalgamation involves the ability of mercury to form compounds of several metals.
Before amalgamation, the nugget should be placed in a solution of nitric acid in a ratio of 10:1 with water. The gold must remain in solution until the visible reaction is complete, after which it must be washed.
For amalgamation, precious metal and mercury are taken in equal proportions. Place both substances in a non-metallic tray and rotate it. A ball of mercury dissolves in the molecules of the nugget. Unnecessary sediment is poured out of the tray.
The amalgam saturated with gold must be washed carefully under running water.
Excess mercury from the amalgam is removed by pressing the ball through wet suede. The compound remaining on the surface is heated until the mercury completely evaporates.
Aqua regia
Most acids have a terrible effect on organic matter. But even in them gold does not dissolve. Lomonosov's famous invention - aqua regia - is the only acid capable of starting the reaction.
Aqua regia is a mixture of hydrochloric and nitric acid in a special ratio (1:3). Its properties are greatly enhanced due to the high concentration of components.
Expert opinion
Vsevolod Kozlovsky
6 years in jewelry making. Knows everything about samples and can identify a fake in 12 seconds
The precious metal dissolves in aqua regia due to the fact that nitric acid oxidizes hydrochloric acid. A special compound is formed - atomic chlorine, which instantly reacts with the metal, creating complex chlorauric acid. Part of the precious metal crystallizes, and the other part dissolves.
It is worth noting that the occurrence of a chemical reaction depends on what acid the metal is dissolved in and what its concentration is.
Bleaching
Chlorine, widely used in everyday life, is an aqueous solution of chlorine gas, which belongs to the group of halogens. For refining, bleach purchased in a regular store is not suitable, because... its concentration is too low.
A concentrated solution of chlorine has the following effect: chlorine breaks down into hydrochloric and hypochlorous acids, the second, in turn, under the influence of sunlight, decomposes into hydrochloric acid and oxygen. As in the reaction with aqua regia, an atomic substance is released that easily oxidizes the nugget.
Iodine itself is an insoluble substance in water. Its compound with potassium iodide dissolves. This is a medicine called Lugol.
Gold dissolves in Lugol due to the fact that iodine creates weak compounds - anions. But the reaction is much slower than with acids, and only the top layer of metal dissolves.
Which method is suitable for home use?
Gold refining (obtaining pure metal) can be done at home. The safest method of dissolution is using electric current.
Electrolysis
A large bath is filled with hydrochloric acid and gold chloride, a reagent used to test products and determine the sample. It can be isolated using aqua regia, gold and ammonia or purchased ready-made in jewelry supply stores.
The reaction, called electrochemical, occurs due to the voltage applied to the bath. As a result, high-grade metal without impurities settles on the sides, and the remaining components precipitate at the bottom of the bath.
Method of using reagents
Reagents for gold can quite accurately determine their sample; they are convenient to use on a large scale, and not at home. Their use for testing begins with inspection of the product. Sometimes one glance at a sample is enough to identify a fake. The mark may contain asymmetrical symbols, curved shapes and images. The next step is to determine whether the alloy belongs to the group of low-grade or high-grade gold.
The surface of the product in a certain place is cleaned. This helps to find out if there is another metal underneath the gold layer or if it is a single alloy. The further procedure depends on the type of reagent chosen.
Gold chloride does not act equally on different compositions. To check the purity, the reagent is applied to the surface of the jewelry. Alloys from 585 to 999 samples will not react in any way to the chemical compound. On products that contain half of the total mass of precious metal, gold chloride will leave a dark stain. If the material has a negligible yellow metal content, less than 50%, the reagent will cause a reaction in the form of severe darkening and the appearance of a precipitate. The lower the sample, the richer the color and stronger the sediment.
When using gold chloride, you need to be very careful and observe the exposure time of the drug on the gold surface. The drop should be small and clearly lie in its place, without spreading throughout the entire product. After completion of the work, the chemical is immediately removed.
Before using reagents, the surface of the product in a certain place is cleaned
Nitric acid is considered the most accessible and common method of testing jewelry. Using a pipette, drop the reagent onto the protected surface and wait a couple of minutes. When the acid hits the alloy below sample 583, the acid causes the release of gas. The lower the gold content, the more bubbling will occur under the drop. After checking, the reagent is immediately wiped off with a small piece of cloth or paper napkin.
Potassium iodide is used in a similar way as the previous reagents. The only thing you need to remember is that the drug only acts on alloys with a base metal content above 80%.
Chemical reactions of various gold samples to reagents
The table below shows the reactions of alloys of various samples to one or another reagent.
| Reagent/Sample | Chlorine gold | Acids | Potassium iodide |
| Below 375 | dirty dark green, gray-green spot | dirty dark green, gray-green spot | — |
| 375 sample | greenish-brown spot | — | — |
| 500 carat yellow gold | light brown spot | the drop remains transparent. Chestnut stain when using 585 sample reagent | — |
| 500 white gold | spots of different shades of brown | spots of different shades of brown | — |
| 585 yellow gold | transparent drop | bright spot | — |
| 585 white gold | golden stain | beige, golden or orange spot | — |
| 750 yellow gold | barely perceptible stain | barely perceptible stain | — |
| 750 white gold | light brown spot | light brown spot | — |
| 800 and 900 samples | — | — | dark red spot |
Safety precautions when working with chemicals
Chemical reagents are quite aggressive substances, so when working with them you must adhere to certain safety rules. This is especially true for the use of acids.
You need to lay a thick fabric on the surface where the testing procedure will take place. Hands are protected with gloves, clothing with an apron. Acids are diluted in a special container, added in a thin stream to distilled water. The liquid may become hot. Before using the composition on gold, it must be cooled.
Application and technique of working with touchstone
In addition to chemical reagents, you can test a sample of a precious metal with a touchstone. The mineral of natural origin belongs to the group of silicon shale and contains about 8% carbon, which gives it a black color. There are also artificial touchstones.
The use of a tool begins with its preparation. The surface is wiped with castor oil, then rubs are applied - dense strips no more than 2-3 mm wide and up to 20 mm long. Vertical lines are applied nearby using standard needles that correspond to a particular sample. The rubs are moistened with reagents and the reaction is observed. A dark precipitate in comparison with the reagent indicates a low gold content in the alloy, a light one, on the contrary, indicates a higher one.
The advantages of testing jewelry on a touchstone are the preservation of its integrity, the testing of any alloys, and the simplicity of the procedure.
Buying reagents for gold will be a justifiable expense if they are used in a workshop or pawnshop. For home testing, less complex materials are suitable. In addition, the person conducting the testing must have certain skills, because reagents are expensive, and their wasteful use can hit your pocket.
Ways and means
They were able to determine the composition of precious metals even before complex analyzers were invented. There are simple but effective methods for testing the gold content of alloys. It is most difficult to distinguish gold-plated products, but even in this case you can choose a method.
Authentication is based on simple chemical reactions, using reagents that can be found in any kitchen or medicine cabinet. They also take into account the physical properties of the substance. These tips will come in handy when purchasing jewelry without accompanying documents.
Smell test
It's worth sniffing the product. A real precious metal should not emit a scent. If you can smell it, it means it's jewelry. Silver and its alloys can also smell like iron.
Some materials used for inexpensive accessories emit odors during oxidation. It is enough to vigorously rub the object in your hands. You can pre-moisten it with plain water.
Identification by sound
You can check the precious metal by the sound of it falling on a hard surface (laminate, countertop, tile). If the ringing is dull and low, it means there is emptiness or foreign objects inside the ring or earring.
This method is not 100% reliable, because not everyone has keen hearing. But for comparison, you can throw a ring into a glass and listen to the ringing sound it makes. Products made from other types of metal do not sound such pure notes.
Testing in light and shadow
Jewelers make jewelry from 3 types of gold - yellow, white and red (pink). The shade of the noble alloy depends on other metals added to pure gold to make it harder. Such satellite metals are called alloys:
- Metal without impurities of bright yellow color.
- The white tint is obtained by alloying with silver, zinc, palladium and other elements.
- Copper as an alloying element produces a pink color.
Regardless of the color, if you look at the jewelry in different lighting (in the shade and in the sun), you will notice that it always shines. The brightness of the shine depends on the gold content in the alloy, which is designated as a breakdown.
Joints and stamps
Joints, numbers and other decorative elements must be clear, especially the proof stamp. It is worth taking a photo of the stamp and examining it carefully under magnification or using a magnifying glass.
There is often a difference in color between the individual links and the lock in the chain. Craftsmen use solder of a higher standard to make connections, which means the color will be slightly different. This is fine.
Rye bread crumb
You need to stick the moistened crumb of rye bread around the golden object. Then wait for the bread slurry to dry completely. After breaking the crust, pull out the ring and inspect its trace.
If dark spots appear inside the crumb, this indicates oxidation of the metal. Noble metal does not oxidize even in alloys. But the method will not work for fake gold-plated silver.
We recommend: How to properly clean flounder before frying, baking or stewing?
Ceramic testing
You can run the jewel across tiles or porcelain. There should be thin traces of gold on their surface. If they are black or gray, they are fake.
Don't press too hard on the item. It is better to “draw” with the clasp or the back of the product. This way, the small scratches that inevitably appear with this method will not be noticeable.
Iodine Trace Analysis
To determine gold using iodine at home, you will need a cotton swab, a plate, alcohol, a cloth and iodine. The product must first be wiped with alcohol.
Dip the stick into the iodine solution and apply it to the object. If the trace is light in color, it is brass or copper. If the spot is dark, it is gold. After the experiment, polishing is necessary to remove marks.
Reaction with vinegar
Gold does not react chemically with vinegar. An object of suspected gold is placed in a container containing this substance. Fake precious metal will change color. Vinegar can be safely used to clean any stains from gold items.
When working with concentrated acid, it is worth remembering safety precautions. Vapors and splashes of the substance irritate the mucous membranes and cause skin burns.
Special reagents
Gold is checked at a pawnshop using a silicon slate (touch stone). After contact, a little precious metal remains on the stone, which reacts with the acid. If the trace has evaporated, it is a fake; if it remains, it is real gold.
Determination by magnet
Gold is diamagnetic, meaning a magnet does not affect it in any way. If the product attracts attention, then it is a fake. A magnetic bar of sufficient size is required; a souvenir bar is not suitable for this purpose.
lapis pencil
A lapis pencil based on silver nitrate on gold should not leave marks. Other metals react with it, causing dark spots to appear. This method is not suitable for fake silver.