If you have purchased a piece of diamond jewelry and doubt that it is real, or are just planning to purchase it, it will not hurt to know how authenticity is checked. Affordable home tests will dispel or confirm suspicions and reduce the likelihood that under the guise and price of a diamond you will be sold a sparkling cheap fake.
What does a real diamond look like?
The most popular, prestigious, expensive and promoted stone is the diamond. Every woman (and some men) dreams of him. The natural raw material for making diamonds is diamonds. They are mined from deposits.
Such crystals have an inconspicuous appearance and irregular configuration. For an ignorant person, this is an inconspicuous stone that does not at all resemble a luxurious sparkling diamond.
A diamond is made of pure carbon, but sometimes it contains impurities of other substances that were around while it was in the ground. The fewer foreign inclusions found in a diamond, the higher its purity. Samples without large inclusions, defects, or cracks are sent to jewelers for processing. To become a full-fledged diamond, the diamond must weigh at least 0.29 carats.
The content of other chemical elements gives diamonds their color. Today, pink, yellow, and blue diamonds are in fashion, but colorless specimens are most valued.
After the jeweler cuts, grinds and polishes the diamond, it becomes a luxurious diamond with the following properties:
- Unsurpassed hardness. The diamond can withstand pressure of several tons. It cannot be scratched. Only another diamond can leave a mark on it. Its hardness is 10/10 on the Moss scale (for gold this figure is 3/10).
- Fragility. "A Girl's Best Friend" doesn't pull any punches. If you hit a diamond hard with a hammer, the stone will crack just like glass.
- High refractive index. When light hits a diamond, the stone flashes with myriads of silvery sparks. Due to strong refraction, the diamond does not shimmer with multi-colored highlights, but scatters a noble glow consisting of shades of gray.
- Dispersion or “play of the stone”. According to this indicator, the diamond is a recognized record holder. No other gemstone produces such intense shine.
- Luminescence. In ultraviolet light, the diamond glows with a soft blue glow.
- Resistant to acids (except hydrofluoric acid).
- Withstands high temperatures. The stone will burn if heated to 850 °C or higher.
- Does not change color or fade. And in a hundred years it will shimmer and shine.
Information about the main qualities of a diamond will help you independently distinguish a diamond from a semi-precious stone if you cannot check it with a jeweler.
Real diamonds look like this:
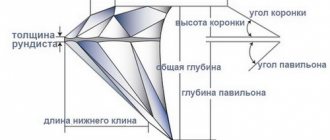
- Faceted stone. If it is unframed, it is accompanied by a certificate confirming its authenticity and quality. If the stone is inserted into the product, then the name (br), clarity (evaluated by four parameters, most often it is 2/4), carat (for example: 1 ct), cut type (cr - round, o - oval) is written on the tag and so on).
- Shimmers and shines. In the light, the stone sparkles with all its facets. This is its distinctive property, which is reflected in the name. Translated from French, “brilliant” means brilliant.
- Has an invisible cut. If it is inserted into a piece of jewelry, it is impossible to see its top and cut angles.
- Sparkles in shades of grey.
- Does not wobble, securely fixed in the product.
- Set in gold or platinum.
- Doesn't shine through. In a properly cut diamond, the bottom is not visible.
- There must be a hole under the stone. The lower part of the diamond (pavilion) should not come into close contact with the metal, because refraction is determined by the stone-air parameter, not the stone-metal parameter.
- Store-bought diamonds often have a round shape and a classic cut of 57 facets.
A black diamond is expensive, but looks less impressive.
It does not play in the light, but only gives an aristocratic glow from the dark surface.
What does the stone look like and where to buy it?
Diamond is a material from which, after processing and cutting, diamonds are obtained. A crystal found in nature is unattractive - a rough surface, dullness, a grayish coating-crust with cracks. However, the pebble is always transparent.
Typically, a diamond crystal is devoid of shades. Sometimes brownish, yellowish, greenish or pale pink specimens are found. A rarity - a natural black mineral. Most gem quality stones are brown or yellow in color.
Getting a natural diamond is either luck or chance, since it does not go on sale. The market is divided between mining companies and specialized exchanges. The price of an average quality natural stone is $510–620 per carat. It depends on global trends.
What can it be easily confused with?
A diamond in a piece can be replaced not only at the jewelry manufacturing stage, but also in a jewelry salon. Counterfeits have been used for a long time; they existed back in 1920. In the past, they tried to pass off radiant or corundite as a diamond. Later, other cheap imitators of the “royal stone” appeared - strontium, rutile, titanium, white sapphire.
Modern technologies have made it possible to create artificial stones that are absolutely identical in appearance to processed diamonds. They are made of such high quality that even testers are not always able to recognize a glass diamond.
The properties of a gemstone are best imitated by the following fakes:
- Cubic zirconia (zircon) is a synthetic stone, zirconium dioxide. It was invented by Soviet physicists in the 70s of the last century. Since then, products with cubic zirconia have been sold all over the world. Zircon shines almost as brightly as a diamond, but with iridescent highlights. It can be transparent (the most expensive) and colored. Currently, cubic zirconia is produced in six main colors.
- Moissanite is carborundum, the most accurate artificial copy of a diamond. It is 90% similar to the precious “prototype”. Its shine is even more intense than that of the “king of stones”. It is impossible to identify moissanite by eye; even an experienced jeweler can make a mistake. Not all testers are up to this task.
- Rock crystal is similar in appearance to a diamond, and after cutting it acquires a dazzling shine. You can recognize an imitation by the following characteristics: rock crystal is set in silver, less often - in gold, a diamond is set only in platinum and gold. Glue is often used to fix crystal, but this is not done when working with diamonds.
The following are also sold under the guise of a processed diamond:
- white topaz;
- yttrium aluminum garnet;
- leucosapphire;
- white beryl;
- artificial diamond;
- transparent spinel;
- rhinestones (ornamental stones made of glass);
- combinations of synthesized stones.
White metal frame enhances shine
Even in ancient times, it was noticed that faceted crystals look most advantageous in a frame made of white metal, which emphasizes the beauty and brilliance of the diamond.
For many years, highly transparent stones were set into items made from silver, which was the whitest known precious metal. Over time, silver tarnishes and black spots appear on it. If you do not clean it regularly, the black product takes on an unpresentable appearance, losing its shine.
For colored (usually yellow-brown) minerals, a red gold setting was perfect, as it enhanced the natural brilliance of the diamonds.
With the invention of the technology for producing palladium, the production of white gold began, which looks much more presentable than yellow and red and perfectly highlights the beauty of precious stones.
The shine of a diamond on a ring, pendant or earrings made of platinum is even more noticeable. This noble silver-gray metal is considered the standard of beauty. Its high price only emphasizes the elitism of the precious stone set in the frame.
Professional authentication methods
A purchased diamond can be checked for authenticity (for a fee) by a jeweler in a workshop or salon that sells items made of precious metals. For express analysis, a diamond detector is used. The check takes 8-10 minutes.
Outdated models of such devices only examine the thermal conductivity of the mineral, and therefore do not always provide reliable information about the authenticity of the stone. This tester will not help identify moissanite because it has the same thermal conductivity as a diamond.
Professional jewelers who specialize in working with diamonds use an advanced diamond authentication tester. He studies the refraction of light. In this indicator, moissanite is ahead of diamond, which makes it possible to immediately detect a fake diamond.
The diamond tester only tests cut crystals.
Such a device will not be able to examine a rough diamond and determine its authenticity.
The most accurate result is guaranteed by the use of three sensors that analyze reflectance, luminescence and photoluminescence. Inexpensive diamond testers give a 50/50 result - “either a diamond or not.” Such devices cannot be trusted.
Experienced jewelers are able to identify a diamond without the use of technology. To distinguish a diamond from a semi-precious imitation or glass, they examine the stone using the following criteria.
Light
Diamonds have special optical properties that are easy to detect by visual inspection in the light or using a magnifying glass with 10x magnification:
- They give the same intense shine not only from above, but from all sides.
- In directed light they scatter with silvery reflections.
- Opaque. Light falling on a smooth surface of a stone is reflected from the edges.
If you look at the stone from above, you will see many iridescences and a tiny dot in the middle - a thorn. There is a simple way to check this property: draw a letter on a piece of paper and try to see it through the mineral. If it's a diamond, you won't see anything.
Comparison
To distinguish a genuine diamond from other stones, it is enough to know a few basic differences:
- A real diamond is a natural formation; it is never absolutely pure. Looking at it through a magnifying glass, you will definitely see the smallest imperfections in it. If the stone has a perfectly smooth and even surface, you have an artificial analogue.
- A cut diamond sparkles and shimmers so much that other stones appear inexpressive and faded against its background. However, it is difficult to distinguish a stone by this indicator. Some artificially synthesized minerals (moissanite) can sparkle no worse than diamonds.
- Diamond is a record holder for strength; after processing, its edges become sharp and clear. In glass imitators they are less sharp and somewhat rounded.
Distortion
A natural diamond does not exhibit double refraction. If you shine light on it and look through a magnifying glass, you will notice that a direct light beam is reflected from its edges. It never splits in two or deviates to the side. If it turns out that one face reflects two rays (flat and inclined), it is cubic zirconia.
Weight
A reliable method that jewelers have long used to assess the authenticity of diamonds is weighing on a carat scale. It is based on the fact that the size of the stone must correspond to the carat weight. It is known that zircons are half as heavy as diamonds, so a fake will be immediately detected.
The weight of precious stones is expressed in carats: 1 ct = 0.2 g. For example: small diamond: 2.0 mm = 0.029 ct; medium: 3.0 mm = 0.098 ct, 5 mm = 0.450 ct; large: 6.5 mm = 1.010 ct, giant at 9 mm = 2.59 ct.
Frame
A diamond is an elite stone, so jewelers are very meticulous about setting it in a product. Depending on the frame, it appears larger or smaller. The frame allows you to hide minor defects and foreign inclusions. Metal, setting and setting are factors that will help distinguish a real cut diamond from a budget fake.
When purchasing diamond jewelry, check it for compliance with the following rules:
- High purity diamonds are usually set in platinum or white gold. It is believed that white metal does not distract attention from the luxurious stone, but only highlights the brilliance and luxury.
- Colored diamonds are set in red or yellow gold. It harmoniously combines with fantasy stone.
- Silver frames are not elite enough and expensive. Cut diamonds are inserted only into jewelry made of precious metals - gold and platinum.
- A diamond is set in one of three ways. A popular type of fastening is using tiny metal claws (prongs). Blind fastening is a reliable method of encrusting products with diamonds, but it visually reduces the size of the mineral. Much less common is corner setting, when the stone is inserted not into a prepared socket, but into the metal plate itself. Other fastening methods are also used, but the underside of the stone is always left open. If the stone is fastened carelessly (loose, too recessed into the frame, the distances between adjacent paws are not the same) - it is not real. Diamonds are not treated this way.
- No adhesive setting is used for natural stones. Artificial crystals are “planted” on the glue.
To make sure the stone is set in platinum or white gold and not silver, check the hallmark of the metal.
Ultraviolet
A more accurate method that will distinguish a diamond or a cut diamond from inexpensive counterparts of artificial origin is based on the use of ultraviolet light. If you have a quartz medical or ultraviolet lamp at home (for drying gel polish), shine it on the stone and evaluate the result:
- Under ultraviolet light, diamonds emit a bluish glow.
- If the stone does not react to exposure to UV rays, it is glass or another imitation diamond.
- The appearance of a green, gray or yellow glow indicates moissanite.
Diamonds have another specific feature - they are invisible in X-rays. But this property cannot be tested at home.
Diagnosis of the stone and its origin
Diagnosis of stones in the MGC laboratory occurs in stages:
- Visual inspection through a gemological triplet loupe allows you to draw preliminary conclusions about the material and nature of the stone. As a rule, it is used at the very initial stage of studying the stone.
- The use of detectors based on the measurement of thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity and refractive index (reflection), allowing the identification of imitations, such as moissanite, cubic zirconia, leucosapphire, etc.
- Visual inspection under ultraviolet light and cathode rays. In some cases, this method can provide information about the nature of the diamond’s origin and possible refining. Therefore, this stage is mandatory in the identification procedure, not to mention that fluorescence is one of the additional factors in assessing a diamond.
- The use of spectral and optical equipment of varying degrees of complexity, which makes it possible to distinguish obviously natural diamonds from rare physical and chemical types of natural diamonds and refined and synthetic stones.
- Optical microscopic study of inclusions, structural inhomogeneities and color distribution. One of the traditional diagnostic methods, requiring highly qualified experts.
- The use of spectral analysis methods such as Raman, luminescence, infrared spectroscopy, spectrophotometry in the visible range of light. This set of methods has the greatest degree of information content.
- Additionally, methods for testing a diamond can be used, such as studying its behavior in an electromagnetic field.
The exact sequence of work and methods for carrying it out will give confidence in the accuracy of determining the nature of the formation of a diamond, the presence or absence of refining, which affect the potential investment attractiveness of the stone.
How to distinguish a diamond from a fake at home
To independently verify the authenticity of a stone, you can use several proven home methods, some of which are also applicable in a jewelry salon.
To get an accurate result, arm yourself with a flashlight and sandpaper. Prepare a magnifying glass with at least 10x magnification. You will need a piece of soft, clean and dry cloth, water and vegetable oil.
It is better to carry out a home examination on a sunny day.
Water
Using water, you can instantly find out whether or not a diamond is set in a ring, earrings or other purchased jewelry. Sprinkle a couple of drops of water onto the top flat surface of the stone. Poke them with a needle. If the drops have not changed, then you were not deceived. On the surface of artificial stones they will disintegrate into small fractions.
To get a more visual picture, take vegetable oil rather than water, put it in a pipette and drop it onto the stone. If the drop remains intact, this will prove the authenticity of the mineral; if it splits into parts, this is a negative sign. They sold you a fake under the guise of a diamond.
Breath
Natural diamonds do not become covered with “perspiration” even at high humidity. Knowing this feature, you can instantly check the stone not only at home, but also in the store before purchasing the product.
To do this, wipe the crystal with a soft flannel cloth and then breathe on it for 2-3 seconds. If it remains dry and shiny, it is a diamond. The fake will fog up, become damp and dull.
Price
Cost is an essential parameter for evaluating a diamond.
Diamonds are the most expensive gemstones. They can't be cheap.
If you are offered an inexpensive diamond ring (at a discount), do not give in to such temptation, otherwise you will invest your money in a worthless thing.
The price of a diamond is calculated from such indicators as the type and quality of cut, carat weight, clarity, color rarity, and current prices on the world market. The cost of such stones directly depends on the size. A 1-carat diamond costs 15-20 times more than a scattering of tiny diamonds with the same total weight.
Scratches
Diamond is a super-strong mineral. It is impossible to scratch it. To ensure that a piece of jewelry is a real diamond, rub the surface of the stone with sandpaper or corundum. If there are no traces left, this is truly the “king of stones.” If roughness or scratches appear on the surface, this is just a skillfully executed fake.
Use this method very carefully to avoid scratching the gold setting of the jewelry. Do not test the hardness of a stone using another diamond; it will easily damage its “brother.”
Prohibited Methods
If you don’t mind ruining a stone imitation of a cut diamond, then you can determine the authenticity of a diamond using cruel methods:
- Keep the stone in the flame of an open fire for 3-4 seconds. If it stays the same, it's a diamond. Moissanite will change color to green, and the original color will not be restored. It will be hopelessly spoiled.
- Drop the crystal into hydrochloric acid. If it is a linden tree, white streaks will form on it. It will no longer be possible to remove these marks. A real diamond will not suffer at all from such testing.
- If you suspect zirconium, lightly run a diamond pencil over the stone. This tool will leave a distinct mark on the semi-precious stone.
When performing this test, do not apply excessive force, otherwise the stone will crack.
The authenticity of a diamond can only be determined using such barbaric methods at home, after it has already been purchased. In a jewelry salon, no one will allow you to throw it into acid or burn it in fire. These testing methods are not suitable for set stones (due to the risk of damaging the jewellery).
Is it possible to buy rough diamonds?
Many jewelry stores have begun offering rough diamonds in addition to polished and faceted diamonds. You can buy such a diamond - either free or set in a piece of jewelry.
So why buy a rough and rough diamond?
On the one hand, they are much cheaper than cut diamonds of similar color and clarity.
And let's not forget that a rough diamond will stand out in appearance, as people are used to seeing mostly polished gemstones in jewelry.
The downside to buying a rough diamond is that its brilliance and sparkle will be much lower than that of a cut diamond.
Why is that?
When a jeweler makes a cut, he shapes the facets so that the light entering the stone reflects off its walls, giving it a more brilliant appearance.
This effect is not present in rough diamonds. So when deciding whether to buy a rough diamond, weigh its unusual appearance and low price against its relative lack of brilliance, and decide which is more important to you.
Authentication Tips
Some more useful information for those who decide to test a rough diamond on their own:
- You can verify the authenticity of the purchased stone in this way: lubricate its surface with vegetable fat and glue it to a window or other glass surface. A real diamond will not fall off, but an artificial one will immediately fall down. The described method is applicable only to unmounted minerals. If the diamond is in a ring or earrings, it will not stay on the glass and will fall under the weight of the metal.
- There is a common myth among people that a high-quality natural diamond is invisible in water. It is not true. No matter how transparent a diamond is, it will still be visible because its density is higher than that of water. But the dive test is still not useless. By lowering the stone into a glass of water, you can check its integrity. If it is glued together from two stones, then the border of the joint will be visible.
- A magnet will help you distinguish a synthetic diamond from a natural one. 90% of artificial crystals are attracted to it.
Only an independent gemologist can accurately distinguish a real diamond from a cheap synthetic fake and support his conclusions with a certificate. This examination is carried out in a special gemological laboratory. If we are talking about a stone weighing 1 carat or more, then it is better not to take risks and turn to professionals.
Modern imitation diamonds copy diamonds so accurately that an ordinary person without special training and expensive equipment will never detect a fake. There are different ways to find out whether a stone actually is an expensive diamond or an ordinary piece of glass, but most of these methods do not provide a 100% guarantee.
Differences between moissanite and diamond
Let's consider another analogue of the “king of stones”, moissanite. It is silicon carbide and has the formula SiC.
Natural moissanite was first discovered at the end of the last century in Arizona. Its discoverer was the French chemist Ferdinand Moissan, who christened the new mineral with his own name.
As it turns out, there is very little natural moissanite on Earth: it is found mainly in the remains of meteorites. As a rule, there are small pebbles that do not have a diamond shine and transparency. The largest nuggets found did not exceed a few millimeters in diameter.
Almost at the same time, Edward Atcherson patented a technology for the synthesis of powdered SiC, which was used primarily in the production of abrasives. It was a synthetic carborundum material, chemically a complete analogue of moissanite.
The invention of the technology for synthesizing jewelry-quality carborundum produced a real revolution. Jewelers received an almost complete analogue of a diamond, which is more than an order of magnitude cheaper than its noble counterpart. However, even synthetic moissanite is much more expensive than cubic zirconia.
Natural moissanite is negligible. So don’t trust sellers: you won’t find jewelry with this naturally occurring mineral. But carborundum is a permanent resident of jewelry store shelves.
It is almost impossible to distinguish moissanite from a diamond at home, at least not for a specialist. All methods that can be applied without the use of special equipment lead to damage to moissanite or require the presence of a natural diamond as a sample.
You can recognize a diamond next to a moissanite by its more subdued shine: the second shines brighter due to its higher refractive index. Moissanite is equally transparent, very refractory, and resistant to aggressive chemicals. Its hardness ranges around 9 on the Mohs scale. This means that it can be scratched with a diamond, but not with anything else.
Gold earrings with diamonds (go to the SUNLIGHT catalogue)
If you don't mind the stone, you can perform a basic thermal test. Apply the flame of a match or lighter to the diamond and moissanite. Both stones will become smoky, but if the diamond appears in its original form after cleaning the carbon deposits, the carborundum will turn green and become cloudy.
Regular cleaning is essential
To maintain the natural shine, diamond jewelry requires special care. Diamonds, even of the highest quality cut, can quickly lose their shine over time and become covered with a white coating, which can only be removed by repeated polishing.
This is especially true for small stones, which quickly become covered with a fatty film and have a weak shine.
Glitter diamond jewelry is best cleaned with gloves. If this is not possible, then try not to touch the gemstone with your fingers. Use soapy water and a soft cloth to clean. Warm water is much better for this than cold water.
When cleaning diamond jewelry, it is prohibited to use excessively hot water and dry it with a hair dryer. Diamonds are afraid of direct sunlight, and if you store rings and earrings in a window, you will end up with stones without a bright shine and a whitish coating within a short time.