What kind of silver is this
Strictly speaking, there is no such type of silver as “technical”. This is the name given to any silver alloy used not in jewelry, but in production.
Composition and properties
The main alloying component in a jewelry alloy is copper. The technical range is wider: cadmium, zinc, tin, nickel, and aluminum may be present. Their proportions are calculated based on the desired result.
Cadmium, zinc and tin lower the melting point, which makes alloys containing them valuable solders. True, cadmium makes the product more expensive, and zinc negatively affects its strength, so there are no universal solders - the composition is selected individually for the task.
Types of silver
It is important to know that silver comes in only one color, which is what this precious metal is and differs from other precious metals, such as gold. There are several types of silver:
- Sterlingov;
- Blackened;
- Oxidized;
- Filigree;
- Matt;
- Coin.
Sterling silver is 925 standard; it is most often used for the production of jewelry, decorative items (figurines, candlesticks), tableware, and dishes. Products made from sterling silver are dazzling white, with a pleasant shine, reliable and durable. This type of silver got its name from the one-pound (1 sterling) silver coin.
Blackened silver is produced by engraving pure silver and then covering it with niello, which is an alloy of silver sulphide, lead, and copper. After the niello is melted, black lines remain on the silver. Blackened silver items do not require cleaning. This type of metal is used to make jewelry, religious objects, amulets, decorative items, and sometimes cutlery handles and decorative elements of utensils are blackened.
Oxidized silver is a fairly new technology (a combination of silver and sulfur), which replaces blackening, while you can achieve the effect of aging silver products, therefore, when buying blackened silver or being offered “antique silver” things, be careful, it is quite possible that They are trying to sell you oxidized silver goods. Of course, this is also silver, but its price should be much lower. Small jewelry is usually made from this metal and is used in the restoration of antiques.
Matte silver is a product coated with enamel. They are used mainly for making jewelry and religious objects. These things look simply great and original. Matte silver is durable.
Filigree silver is produced by rolling metal into the thinnest threads, thanks to the plastic properties of silver, then the most beautiful original products are created from these threads, the work is mostly done by hand.
Coin silver – as the name suggests, it is used to make commemorative and collectible coins.
Metal samples and its alloys
Usually, pure silver is not used in the production of jewelry, due to the softness of the metal; most often it is alloyed with other chemical elements that give silver additional strength qualities. Most often they use a silver-copper alloy, alloys with aluminum, nickel, cadmium, and zinc.
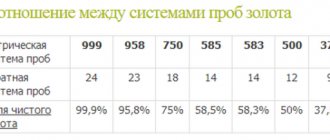
The International Metric System divides silver into the following hallmarks:
- 800; 830 – used in the production of cutlery, body parts, writing instruments, and some decorative items;
- 875 – cutlery, serving items;
- 916 - today this sample is rarely used; previously, household items, cutlery, decorative items, and jewelry were created from such silver;
- 925 is the most popular and common standard of silver metal, from which almost any thing is made today - jewelry, cutlery, decorative items;
- 960 – production of filigree, various original and artistic works;
- 999 – or pure silver, which is used for silvering dishes, jewelry, in the food and medical industries.
In order to know what standard a particular product is, it is usually branded.
Take a look at some of the marks that were used in past years and that are used now:
Where is it contained?
Technical alloys are used to create much of what we use every day. If you are reading this article at work, look around and look at the office equipment - there is silver in every device and microcircuit. One power supply contains 1.5 g.
The more modern the device, the less precious metals it contains and, accordingly, the more difficult it is to extract them.
The state controls the disposal of equipment not only for reasons of environmental safety, but also to reduce the loss of precious metals during processing. Only licensed organizations can accept high-tech scrap containing precious metals from the population—for example, there are several dozen of these in Moscow.
Silver in Valheim: how to get it, how to find it, what it looks like
Now the tenth world of Norse mythology, presented in the game Valheim, is extremely popular. And in this regard, it is regularly replenished with completely new players. And since many of these users are aspiring Vikings, you have to discover for yourself how the world of Valheim is an incomprehensible place. Therefore, you will have to figure out many details here yourself. After all, here even a basic search for a certain ore is a real problem. Yes, we have a separate guide for newcomers to the game Valheim , but it does not talk about game currency.
As a result, it’s difficult to figure it out on your own, especially when it comes to searching for silver. This metal in the game can safely be considered elite. In the later stages of the game it is impossible to do without silver, and during the search process not only hostile enemies will interfere, but also the weather.
How to determine authenticity
The composition of a part or coating is determined by GOSTs. But there are no such concepts as “genuine” and “fake” technical silver - for two reasons:
- For each purpose, a different alloy is selected. Impurities in it change the properties of the base, and “purer” does not always mean “better” here.
- It is not economically feasible to counterfeit the precious metal used in microcircuits and switches.
If you accidentally come across a homemade “technical” ingot and are wondering if it is silver, try using a magnet on it (a high-grade alloy will not be attracted) or rubbing it in your hand with chalk (the chalk should darken).
Application of silver in the electrical industry
The metal that is used in the production of parts and elements for the electrical industry is called technical; it is most often pure 999 silver; sometimes alloys of silver with other substances are used. Electrical silver must have excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and light reflection. It is used to make silver wire, solders, high-quality electrical contacts, silver-plated conductive contacts and other critical parts.
The following items are made from silver or silver plated:
- Connectors;
- Diodes;
- Transistors;
- Resistors;
- Microcircuits;
- Ceramic capacitors;
- Contact relays;
- Resistance;
- Circuit breakers;
- Rechargeable batteries;
- Monocore cables.
Silver is an exhaustible type of natural resource, deposits are being depleted, but the metal is in demand, and not only for the production of jewelry, but also necessary for various industries, so today, recycling of this noble metal is more important than ever.
How is it different from jewelry silver?
The differences between a technical alloy and a jewelry alloy lie in its purpose and variety. Theoretically, you can cast yourself a ring or pendant from a high-grade alloy obtained by refining silver from parts.
But there is a danger: the law provides for criminal liability for unauthorized extraction of precious metals, even if the raw material is your own computer.
Why are gold and other precious metals used in equipment?
Gold, platinum, silver, as well as other valuable metals (copper, brass, etc.) are unsurpassed conductors, which ensures the uninterrupted functioning of high-tech computer and other devices.
In addition to this technical parameter, precious metals do not oxidize .
This characteristic, in turn, directly affects a significant increase in the service life of the same high-tech devices, which include various equipment:
Where to submit
You will not be able to sell technical silver legally at a market price. They will turn a blind eye to a small amount of technical shavings, but if you start collecting raw materials seriously and try to sell a significant amount - for example, 200 g - you will face prosecution under Art. 191 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Nevertheless, many are engaged in melting metals without a license, having equipped a workplace in their dacha or garage. Perhaps jewelry making will captivate you so much that you will begin to create unique jewelry (which a private individual can own).
Characteristics and properties
Material properties:
- Metal color: silver-white. A black coating may be observed in cracks, chips, and recesses.
- The more impurities a material contains, the faster it oxidizes in open air.
- Hardness index - up to 3 on the Moss scale.
- Density indicator - up to 12.
- Melting point - 961°C.
- Boiling point - 2162°C.
- High ductility and thermal conductivity.
Cutlery and jewelry cannot be made from pure silver because the metal is very soft. Most often, jewelry is made from an alloy of silver (92%) and copper (8%).
This material cannot be called toxic, but if you take drugs with a high content of it and do not follow the dosage, you can harm the body. Various unpleasant symptoms may develop:
- conjunctivitis, irritation of mucous membranes;
- change of normal skin color to purple;
- the appearance of spots on the face.
If you continue to use drugs with a high content of this metal, it will gradually accumulate in the body and combine with other trace elements. This will lead to a rapid deterioration of the general condition.
Jewelry with silver (Photo: Instagram / serebro_blesk_26)
How to remove from radio components
To extract silver from electronic scrap (for example, a relay or microswitch of the MP type), you need to determine which parts (contacts) contain silver and carefully separate them with wire cutters or scissors (depending on the strength of the material). The radio alloy is approximately 817 fine, and one relay will reward you with 0.5–3 g of the noble metal.
You can see what a typical microswitch containing silver looks like in the photo.
Cleaning silver from impurities
Refining at home is difficult: reagents are available in stores, but they are toxic. Follow safety precautions:
- put on a protective mask and gloves;
- take care of ventilation or work outdoors;
- When preparing a solution, pour the acid into the water, and not vice versa.
Purification methods are based on the dissolution of the feedstock in acids (nitric, sulfuric) followed by reduction from chloride. The result will be a metal with a breakdown of about 980, which can be further purified electrolytically, resulting in an almost pure element.
Properties of silver.
Also on topic:
METAL SCIENCE PHYSICAL
Pure silver is a relatively soft and ductile metal: from 1 g of silver you can draw the thinnest wire almost 2 km long! Silver is a rather heavy metal: in density (10.5 g/cm3) it is only slightly inferior to lead. In terms of electrical and thermal conductivity, silver has no equal (that’s why a silver spoon in a glass of hot tea heats up quickly). Silver melts at a relatively low temperature (962° C), which greatly facilitates its processing. Silver can be easily alloyed with many metals; small additions of copper make it harder, suitable for the manufacture of various products.
“Silver does not oxidize in air,” wrote D.I. Mendeleev in his textbook Fundamentals of Chemistry
, – and therefore is classified as a so-called noble metal. It has a white color, much purer than all other known metals, especially when it is of chemical purity... Chemically pure silver is so soft that it wears off very easily...” But although silver does not react directly with oxygen, it can dissolve significant the amount of this gas. Even solid silver at a temperature of 450° C can absorb five times the volume of oxygen. Significantly more oxygen (up to 20 volumes per 1 volume of silver) dissolves in the liquid metal.
This property of silver leads to the beautiful (and dangerous) phenomenon of silver spattering, which has been known since ancient times. If molten silver has absorbed significant amounts of oxygen, then the solidification of the metal is accompanied by the release of large amounts of gas. The pressure of the released oxygen breaks the crust on the surface of the solidifying silver, often with great force. The result is a sudden explosive spatter of metal.
At 170° C, silver in air is covered with a thin film of Ag2O oxide, and under the influence of ozone, higher oxides Ag2O2 and Ag2O3 are formed. But silver is especially “afraid” of iodine, for example, tincture of iodine and hydrogen sulfide. Many homes have silver (or silver-plated) items - old coins, spoons, forks, glass holders, rings, chains, and other jewelry. Over time, they often fade and may even turn black. The reason is the action of hydrogen sulfide. Its source can be not only rotten eggs, but also rubber and some polymers. In the presence of moisture, silver easily reacts with hydrogen sulfide to form a thin sulfide film on the surface: 4Ag + 2H2S + O2 = 2Ag2S + 2H2O; Due to the unevenness of the surface and the play of light, such a film sometimes appears rainbow-colored. Gradually the film thickens, darkens, turns brown, and then black. Silver sulfide is not destroyed by strong heating and does not dissolve in acids and alkalis. A not very thick film can be removed mechanically by polishing the object with toothpaste or powder with soapy water.
To protect the surface of silver from darkening, it is passivated - covered with a protective film. To do this, a well-cleaned product is immersed for 20 minutes in a slightly acidified 1% solution of potassium dichromate K2Cr2O7 at room temperature. The resulting thin film of Ag2Cr2O7 protects the surface of the silver.
Silver easily dissolves in nitric and hot concentrated sulfuric acid: 3Ag + 4HNO3 = 3AgNO3 + NO + 2H2O; 2Ag + 2H2SO4 = Ag2SO4 + SO2 + 2H2O. Silver also dissolves in concentrated hydroiodic and hydrobromic acids, and in the presence of oxygen, in hydrochloric (hydrochloric) acid; the reaction is facilitated by the formation of complex silver halides: 2Ag + 4HI = 2H[AgI2] + H2
Where can you buy or sell
There are organizations involved in purchasing, including technical silver, online auctions, and pawnshops. Most of them operate illegally (without a license), and an attempt to sell independently mined silver may come to the attention of the Department for Combating Economic Crimes (OBEP).
How much does 1 gram of tech cost? silver for today
The value of silver on the world market is rising and today it is considered a good investment. A chart will help you track price fluctuations.
| Price 999 standard according to the Central Bank | Market value of the sample today | Scrap price | Price in jewelry |
Radiant silver
During Soviet times, military factories often used irradiated silver. This is a special type of technical silver coated with radium. Radium is a toxic and radioactive element and has a slight glow-in-the-dark effect. Therefore, it is used in military affairs, for example, for illuminating aircraft instruments.
Radium was added to industrial silver, and such scrap should not have ended up on the recycling market, but it did. It was illegal, but such silver was mined and melted down into products. After some time they stopped producing it, but when buying scrap silver you should be careful, and it is better to have a dosimeter with you.
What is technical silver
Despite the name, which hints at the low quality of the material, this term hides pure 999 silver, an alloy with the addition of copper, or metal-ceramic composites.
It is mined from lead ores and often does not look very attractive.
Ligatures added to technical silver have a strictly defined composition. It is selected according to the application's required adjustments to the chemical and physical properties of the metal and is usually intended to increase the electrical conductivity or strength of the element.
In the manufacture of jewelry, completely different impurities are used, giving the material a more attractive appearance and malleability, which also determines the lower cost of the technical alloy.
Sources of recycled silver
The main sources of secondary silver are products from the electrical and radio engineering industries, printing, photography and film industries, products from the mirror, jewelry and watch industries.
From the household sector, sources of precious metal include scrap jewelry , awards and coins.
In radio and electrical engineering, the following are suitable for silver extraction :
- radio components;
- relay;
- contacts of automatic switches and starters;
- batteries;
- contact relays and ceramic capacitors.
Certain types of solders and contacts can contain up to 99% Ag.
Batteries and resistors
Silver-zinc batteries of the SC series, in which the anode is made of pressed silver oxide powder, are distinguished by a high specific silver content.
For example, the battery of the STs-25 model, weighing 470 g (together with the filled electrolyte), contains 85.5 g of Ag, and the STs-110 model, weighing 1.6 kg, contains 559.783 g of Ag.
In small quantities, technical silver is found in the most common resistors of Soviet times, the MLT series (an abbreviation for “metal film varnished heat-resistant”). For example, an MLT-2 product weighing 2.5 grams contains 5 mg of Ag, which corresponds to 0.16% by weight.
Capacitors and relays
Due to the small size and light weight characteristics of radio components containing silver, it is customary to estimate the amount of Ag in terms of 1000 pieces of each group of radio products.
For some types of capacitors and relays, the Ag content per 1000 pcs. following:
- capacitor K15-5 - about 29.9 g;
- capacitor K10-7V - about 13.6 g;
- relay RES6 – 157 g;
- RSCh52 – 688 g;
- RVM – 897
Films
The printing, photography and film industries “provide” worn and damaged film reels and photo prints .
The main raw materials for extracting precious metals are silver bromide and silver sulphide, ash from photographic paper and photographic prints.
Photographic and film films contain silver, the content of which is standardized per 1 square meter. meter _ For example, every sq. a meter of Micrat 300 film contains 4.68 grams of Ag.
Other devices and items
Silver “secondary” coming from the chemical industry is represented by spent catalysts containing up to 80% Ag, sludge, contact masses and scrap silverware.
Silver-containing waste from jewelry production is generated during machining, smelting and chemical processing of precious metals.
In their composition , they are much poorer than scrap silver and contain from 0.5 to 10% silver, while silver scrap precious metal can contain over 90% (in the case of high-grade jewelry).
Where is silver found?
Today, any owner has the right to remove a silver part from the equipment and sell it. The most valuable, from this point of view, will be old-style mechanisms, for example, electromagnetic starters: they contain precious metal soldering.
The material without impurities is found in common types of relays, temperature sensors (silver wire), SC batteries and amalgam.
It can be found in very small quantities in aircraft wires and connectors.
To check the authenticity of the metal, many use a mixture of nitric acid and potassium bichromate: if the silver is real, the area moistened with the composition will turn red.